Shopping Cart
- Remove All
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $40 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $89 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $122 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $228 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $343 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $497 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $98 | In Stock |
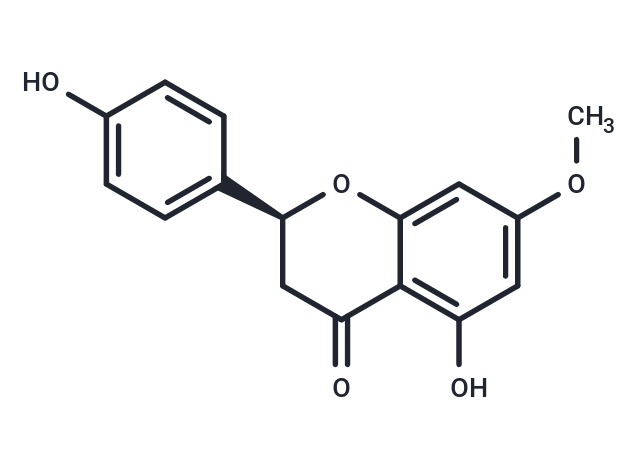
| Description | Sakuranetin, a flavanone phytoalexin from ultraviolet-irradiated rice leaves, it has antifungal, antimutagenic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects |
| In vitro | Young rice leaves in a resistant line exhibited hypersensitive reaction (HR) within 3 days post inoculation (dpi) of a spore suspension, and an increase in Sakuranetin was detected at 3 dpi, increasing to 4-fold at 4 dpi. In the susceptible line, increased Sakuranetin was detected at 4 dpi, but not at 3 dpi, by which a large fungus mass has accumulated without HR. Induced expression of a PA biosynthesis gene OsNOMT for naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase was found before accumulation of Sakuranetin in both cultivars. The antifungal activity of Sakuranetin was considerably higher than that of the major rice diterpenoid PA momilactone A in vitro and in vivo under similar experimental conditions. The decrease and detoxification of Sakuranetin were detected in both solid and liquid mycelium cultures, and they took place slower than those of momilactone A. Estimated local concentration of Sakuranetin at HR lesions was thought to be effective for fungus restriction, while that at enlarged lesions in susceptible rice was insufficient[1] |
| Molecular Weight | 286.28 |
| Formula | C16H14O5 |
| Cas No. | 2957-21-3 |
| Storage | keep away from moisture Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 125 mg/mL (436.64 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.