Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

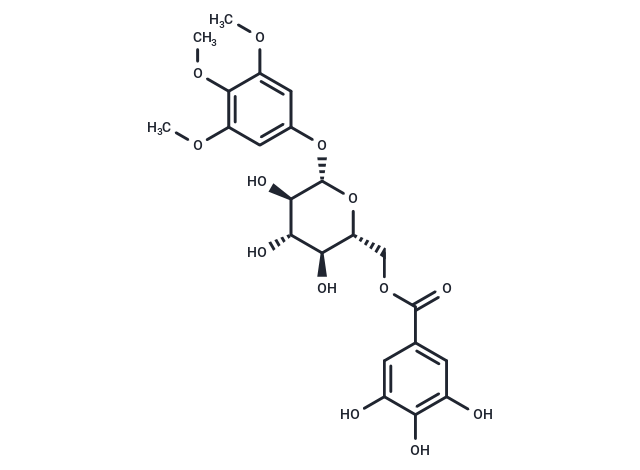
3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl-(6'-O-galloyl)-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside exhibits in vitro antiplasmodial activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $660 | Backorder |
| Description | 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl-(6'-O-galloyl)-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside exhibits in vitro antiplasmodial activity. |
| Molecular Weight | 498.43 |
| Formula | C22H26O13 |
| Cas No. | 109206-94-2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.516 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.