Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

ARN272 is a FAAH-like anandamide transporter (FLAT) inhibitor (IC50: 1.8 μM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $113 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $178 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | ARN272 is a FAAH-like anandamide transporter (FLAT) inhibitor (IC50: 1.8 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | Anandamide transporter:1.8 μM |
| In vitro | FLAT inhibition by ARN272 appeared to be selective because the compound had little or no inhibitory activity on several endocannabinoid-metabolizing enzymes. Moreover, ARN272 produced only weak and incomplete inhibition of rat brain FAAH activity and was not significantly hydrolyzed after incubation with recombinant human FAAH-1 (≈5% hydrolysis after 24h at 37°C) [1]. |
| In vivo | Administration of ARN272 (1 mg/kg, intraperitoneal, i.p.) in mice increased plasma levels of anandamide without changing the levels of 2-AG, OEA or PEA. The inhibitory effects of ARN272 on anandamide internalization in vitro and anandamide deactivation in vivo, along with the diminished anandamide accumulation observed in faah-1?/? mice [1]. The systemic administration of ARN272 produced a dose-dependent suppression of nausea-induced conditioned gaping in rats and produced a dose-dependent reduction of vomiting in shrews. The systemic co-administration of SR141716 with ARN272 (at 3.0?mg/kg) in rats produced a complete reversal of ARN272-suppressed gaping at 1.0?mg/kg. SR141716 alone did not differ from the vehicle solution [2]. |
| Animal Research | All rats were surgically implanted with intra-oral cannula under isoflurane anaesthesia. Following recovery from surgery (3 days), rats received a single adaptation trial to habituate them to the chamber and the infusion procedure. During the adaptation trial, rats were placed individually in the TR chamber and received a 2?min intra-oral infusion of water (reverse osmosis water infused at 1?mL/min). On the following day, rats received the first of two conditioning trials (separated by 72?h). On each conditioning trial, rats received a pretreatment injection of ARN272 or VEH 120?min prior to the conditioning trials. During conditioning trails, rats were intra-orally infused with a saccharin solution (0.1%) for 2?min (1?mL/min) and orofacial and somatic reactions were recorded on video. Immediately following the saccharin infusion, the rats were injected with LiCl (0.15?M) or saline, and then returned to their home cage. Two additional groups were added (after ARN272 at 3.0?mg·kg?1 attenuated gaping) where pretreatment of ARN272 at 3.0?mg·kg?1 or VEH was given 120?min prior, and with SR141716 30?min prior, to each conditioning trial. The groups were VEH-Saline (VEH-SAL), n = 9; VEH-LiCl, n = 8; 0.1?mg/kg ARN272-LiCl, n = 9; 1.0?mg/kg ARN272-LiCl, n = 8; 3.0?mg/kg ARN272-LiCl, n = 8; 1.0?mg/kg SR-3.0?mg/kg ARN272, n = 8; 1.0?mg/kg SR-VEH, n = 8. Seventy-two hours following the second conditioning trial, the rats received a drug-free TR test. During the TR test, rats were re-exposed to a 2?min intra-oral infusion of saccharin solution and their orofacial and somatic responses again recorded. All video recordings were later scored by a rater blind to the experimental conditions using ‘The Observer'. Following the TR test, the rats were returned to their home cages and at 16:00?h, their water bottles were removed to begin a water deprivation regime in preparation for the CTA test.At 08:00?h the following morning, the rats received a one-bottle test in which a graduated tube of 0.1% saccharin solution was placed on the home cage, and the amount consumed was recorded at 30 and 120?min intervals. A one-bottle test was used as there is evidence to suggest it is more sensitive in detecting between-group differences in strength of taste avoidance than a two-bottle test where both water and saccharin are made available [2]. |
| Alias | ARN 272 |
| Molecular Weight | 432.47 |
| Formula | C27H20N4O2 |
| Cas No. | 488793-85-7 |
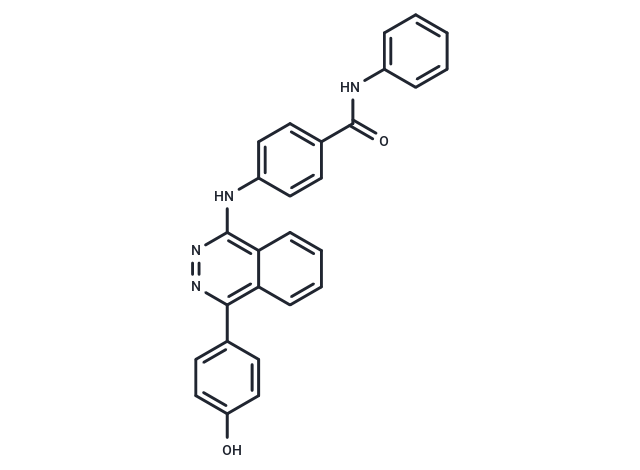
| Smiles | Oc1ccc(cc1)-c1nnc(Nc2ccc(cc2)C(=O)Nc2ccccc2)c2ccccc12 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble Ethanol: 8 mg/mL (18.50 mM) DMSO: 50 mg/mL (115.61 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.