Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867), a synthetic broad spectrum fluoroquinolone antibiotic, inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase. It is more active against Gram-negative bacteria than Gram-positive bacteria.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $59 | In Stock |
| Description | Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867), a synthetic broad spectrum fluoroquinolone antibiotic, inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase. It is more active against Gram-negative bacteria than Gram-positive bacteria. |
| In vivo | Ciprofloxacin (1 mg/L) induces GST activity, in contrast with inhibited GST and CAT of larvae exposed to enrofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin (≥10 μg/L) and enrofloxacin are ecotoxic for development, growth, detoxifying, and oxidative stress enzymes in anuran amphibian larvae[4]. Ciprofloxacin (CIP) shows potent activity against Y. pestis with MIC90 of 0.03 μg/mL[2]. In a murine model of pneumonic plague, ciprofloxacin (30 mg/kg, i.p.) results in a drug exposure which is similar to the drug exposure observed in humans following a 500 mg dose of oral ciprofloxacin. Intraperitoneal ciprofloxacin reduces the lung bacterial load compared to controls treated with intraperitoneal PBS[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | The in vitro kinase assays is performed by incubating purified kinase (IKKε or TBK1) in kinase buffer containing 25 mM Tris (pH7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 10 μM ATP for 30 minutes at 30°C in the presence of 0.5 μCi γ-[32P]-ATP and 1 μg MBP per sample as a substrate. The kinase reaction is stopped by adding 4x sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer and boiling for 5 minutes at 95°C. Supernatants are resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and analyzed by autoradiography using a Typhoon 9410 phosphorimager. |
| Alias | Ciproxan, Ciprobay, Bay-09867, Bay o 9867 |
| Molecular Weight | 331.34 |
| Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| Cas No. | 85721-33-1 |
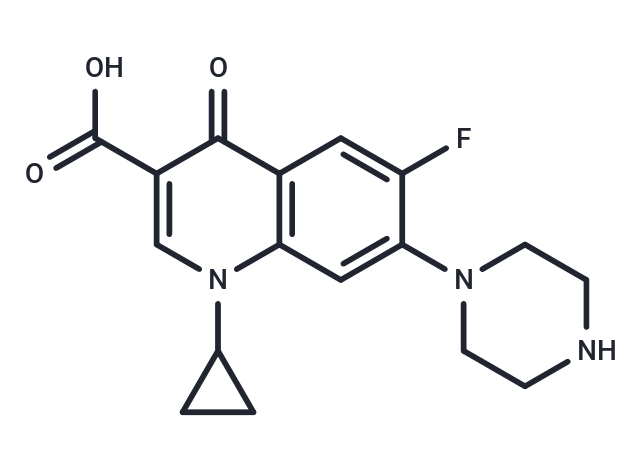
| Smiles | OC(=O)C1=CN(C2CC2)C2=C(C=C(F)C(=C2)N2CCNCC2)C1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.461 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 0.33 mg/mL (1 mM), Sonication is recommended. 0.1 M HCl: 2 mg/mL (6.04 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/0.1 M HCl
0.1 M HCl
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.