Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Rocaglamide (Roc-A), isolated from the genus Aglaia, can be used to treat coughs, injuries, asthma, and inflammatory skin diseases. It is a potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation in T-cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 μg | $600 | In Stock |
| Description | Rocaglamide (Roc-A), isolated from the genus Aglaia, can be used to treat coughs, injuries, asthma, and inflammatory skin diseases. It is a potent inhibitor of NF-κB activation in T-cells. |
| Targets&IC50 | HSF1:50 nM |
| In vitro | Rocaglamide is a potent and selective heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) activation inhibitor with an IC50 of ~50 nM. Rocaglamide inhibits the function of the translation initiation factor eIF4A. Rocaglamide also has anticancer properties in leukemia [1,2,3]. Treatment with Rocaglamide alone leads to apoptosis in 9% HepG2 and 11% Huh-7 cells and treatment with TRAIL induces apoptosis in 16% HepG2 and 17% Huh-7 cells. However, the combination of Rocaglamide and TRAIL induces apoptosis in 55% HepG2 and 57% Huh-7 cells, which is evidently more than an additive effect [2]. |
| In vivo | Tumor volumes in the Rocaglamide-treated group are 45±12% of those in the control group, indicating significant suppression of tumor growth. Rocaglamide treatment shows no reduction in body weight and no apparent signs of toxicity in the mice during the treatment [2]. |
| Cell Research | HepG2 and Huh-7 cells (1×10^4/well) are seeded in 96-well plates in complete culture medium and incubated for 24 h. The cells are then exposed to 100 nM Rocaglamide and/or 100 ng/mL TRAIL for 24 h. The control cells are treated with DMSO at a concentration equal to that used for the drug-treated cells. The complete culture medium is then removed and MTT (200 μL, 0.5 mg/mL in 10% FBS-containing DMEM) is added to each well and the plate is incubated for 2 h at 37°C in a humidified incubator. The solution is then removed from the wells and 200 μL DMSO is added to each well prior to agitation. The absorbance at 570 nm is read using a microplate reader (Bio-Tek ELx800). The value for the vehicle-treated cells is considered to indicate 100% viability. Furthermore, a crystal violet assay is carried out. Briefly, the cells (1×10^5/mL) are seeded in a 12 well plate for 12 h and treated with TRAIL (0-100 ng/mL) and/or RocA(1-100 nM) for 12 h. The treated cells are washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min, and stained using crystal violet for a further 30 min [2]. |
| Animal Research | The Huh-7 cells (3×10^6), suspended in 100 μL mix (equal volumes of DMEM and Matrigel), are implanted subcutaneously into the right flank of 10 female SCID mice (6-week-old) and then randomly divided into two equal groups, one of which received an intraperitoneal injection of Rocaglamide (2.5 mg/kg in 80 μL olive oil; n=5) and the other, used as a vehicle control, received olive oil alone (n=5). These treatments are performed once daily for 32 days and the tumor volumes and body weights of the animals are measured twice a week. The tumor volumes (mm3) are calculated using the following formula: Tumor volume=LS2/2, where L is the longest diameter and S is the shortest. At the end of the experiments, the mice are sacrificed and tumor samples are harvested, fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin as tissue sections for immunohistochemical analysis [2]. |
| Alias | Rocaglamide A, Roc-A |
| Molecular Weight | 505.56 |
| Formula | C29H31NO7 |
| Cas No. | 84573-16-0 |
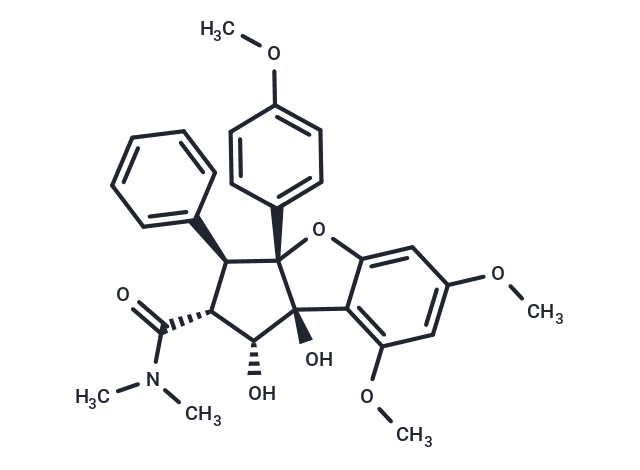
| Smiles | COc1ccc(cc1)[C@@]12Oc3cc(OC)cc(OC)c3[C@]1(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]([C@H]2c1ccccc1)C(=O)N(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.321g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 10 mg/mL (19.78 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 5 mg/mL (9.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.