Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sulforaphane is a natural isothiocyanate that activates Nrf2 and inhibits AMPK-dependent signaling. Sulforaphane has antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities by increasing the transcription of tumor suppressor proteins and inhibiting histone deacetylase activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $109 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $197 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $289 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $713 | In Stock |
| Description | Sulforaphane is a natural isothiocyanate that activates Nrf2 and inhibits AMPK-dependent signaling. Sulforaphane has antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities by increasing the transcription of tumor suppressor proteins and inhibiting histone deacetylase activity. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human colorectal cancer cells HT29 were treated with Sulforaphane (15 µM) for 24-96 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. RESULTS: Sulforaphane at 15 µM was able to inhibit cell growth and induce cell death. 75% of the cells were already dead at 24 h, and almost all of them were dead at 96 h. [1] METHODS: Gastric cancer cells BGC-823 and MGC-803 were treated with Sulforaphane (5-10 µM) for 48 h. The expression levels of target proteins were measured by Western Blot. RESULTS: When gastric cancer cells were treated with Sulforaphane, the expression levels of cell cycle regulatory proteins such as p53 and p21 were increased in a dose-dependent manner, whereas the expression level of S-phase related protein CDK2 was significantly decreased. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the anti-inflammatory activity, a single dose of Sulforaphane (50 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to BALB/c mice. Three days later, LPS was injected to induce acute lung injury (ALI). RESULTS: Sulforaphane significantly reduced LDH activity, lung wet-to-dry ratio, serum IL-6 and TNF-α levels, and NF-κB protein expression in mice with LPS-induced acute lung injury.Sulforaphane exerted its protective effect on LPS-induced ALI through the Nrf2/ARE pathway. [3] |
| Cell Research | HT29 cells are seeded at low density (5×10^4 cells/mL) in 35- or 120-mm diameter Primaria dishes in standard medium containing 5% FCS. One day after seeding, the medium is changed, and HT29 cells are treated with sulforaphane (0-30 μM). An equivalent amount of the solvent (ethanol) is added to control cells (0.2% final concentration). The drug effect on cellular viability is evaluated using the MTT assay [1]. |
| Animal Research | At age 47, 48, 49, 50, and 51 days, each animal receives by gavage either 0.5 mL of Emulphor EL-620 alone or the specified doses (75, 100, or 150 μM daily) of sulforaphane or compound 2, 3, or 4 in 0.5 mL of Emulphor EL-620. On day 50, 3 hr after administration of the vehicle or protector, all rats also receive an intragastric instillation of 8.0 mg of DMBA dissolved in 1.0 mL of sesame oil. This dose of DMBA is selected to produce a substantial tumor incidence, but not one so high as to overwhelm a potential chemoprotective effect. The animals are examined once weekly for the appearance and location of palpable tumors. At age 202 days, i.e., 152 days after carcinogen administration, all animals are euthanized with ether and weighed. The tumors are separated from the fat and connective tissue by dissection weighed and fixed in buffered 10% formalin. All tumors are identified microscopically by examination of stained sections [3]. |
| Molecular Weight | 177.29 |
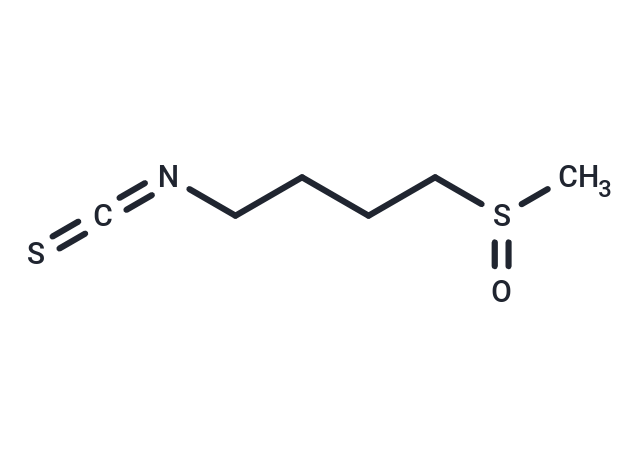
| Formula | C6H11NOS2 |
| Cas No. | 4478-93-7 |
| Smiles | C(CCN=C=S)CS(C)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.17g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 5.5 mg/mL (31.02 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. 5% DMSO+95% Saline: 2.89 mg/mL (16.3 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (310.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10% DMSO+90% Saline/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.