- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Fulvic Acid
Catalog No. T38108Cas No. 479-66-3
Fulvic Acid is a natural product of humus produced by microorganisms in soil, sediment or aquatic environments. Fulvic acid is a phenolic acid and fungal metabolite isolated from Penicillium for the first time. Fulvic Acid inhibits the dimerization of amyloid b (17-42) (AB17-42), destroys the pre-formed trimer of AB17-42, and binds to the catalytic site of phosphodiesterase 5A (PDE5A), which can regulate the body's immune system, affect the oxidation state of cells, and improve gastrointestinal function. Fulvic Acid can be used as an oxidant or reducing agent and has the potential to study chronic inflammatory diseases such as diabetes.
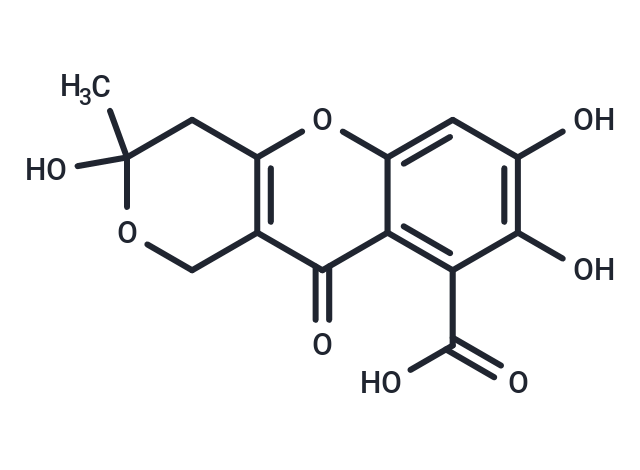
Fulvic Acid
Catalog No. T38108Cas No. 479-66-3
Fulvic Acid is a natural product of humus produced by microorganisms in soil, sediment or aquatic environments. Fulvic acid is a phenolic acid and fungal metabolite isolated from Penicillium for the first time. Fulvic Acid inhibits the dimerization of amyloid b (17-42) (AB17-42), destroys the pre-formed trimer of AB17-42, and binds to the catalytic site of phosphodiesterase 5A (PDE5A), which can regulate the body's immune system, affect the oxidation state of cells, and improve gastrointestinal function. Fulvic Acid can be used as an oxidant or reducing agent and has the potential to study chronic inflammatory diseases such as diabetes.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $88 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $132 | In Stock |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Contact us for more batch information
Resource Download
Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | Fulvic Acid is a natural product of humus produced by microorganisms in soil, sediment or aquatic environments. Fulvic acid is a phenolic acid and fungal metabolite isolated from Penicillium for the first time. Fulvic Acid inhibits the dimerization of amyloid b (17-42) (AB17-42), destroys the pre-formed trimer of AB17-42, and binds to the catalytic site of phosphodiesterase 5A (PDE5A), which can regulate the body's immune system, affect the oxidation state of cells, and improve gastrointestinal function. Fulvic Acid can be used as an oxidant or reducing agent and has the potential to study chronic inflammatory diseases such as diabetes. |
| In vitro | Fulvic acid (15 mg/L) enhanced growth and achieved the highest EPA content (13.9%) in the evolved diatom. Fulvic acid enhanced antioxidant potential and unprecedently governed the expression of PUFA and lipid biosynthetic genes. This investigation demonstrates the efficacy of adaptive evolution empowered by fulvic acid.[1] Embryogenic cell masses (ECM) of Abies cephalonica were grown on proliferation media in the presence and absence of fulvic acid (FA), FA increased the proliferation rate, especially during the early sampling days, and the percentage of PEM in their advanced developmental stage. During the maturation phase, fulvic matter also induced a delay in somatic embryo formation. The structure-activity relationship observed here suggests that the influence of FA on ECM may be attributed to specific bioactive molecules that are preferentially released from the FA loose superstructure.[2] |
| Molecular Weight | 308.24 |
| Formula | C14H12O8 |
| Cas No. | 479-66-3 |
| Smiles | CC1(O)Cc2oc3cc(O)c(O)c(C(O)=O)c3c(=O)c2CO1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.79 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 3.08 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. Methanol: Soluble Chloroform: Soluble | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Keywords
Related Tags: buy Fulvic Acid | purchase Fulvic Acid | Fulvic Acid cost | order Fulvic Acid | Fulvic Acid chemical structure | Fulvic Acid in vitro | Fulvic Acid formula | Fulvic Acid molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



