Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Procaine hydrochloride (Novocaine HCl) is the hydrochloride salt form of procaine, a benzoic acid derivative with local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic properties. Procaine binds to and inhibits voltage-gated sodiumchannels, thereby inhibiting the ionic flux required for the initiation and conduction of impulses. In addition, this agent increases electrical excitation threshold, reduces rate of rise of action potential and slows nerve impulse propagation thereby causing loss of sensation.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $40 | In Stock |
| Description | Procaine hydrochloride (Novocaine HCl) is the hydrochloride salt form of procaine, a benzoic acid derivative with local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic properties. Procaine binds to and inhibits voltage-gated sodiumchannels, thereby inhibiting the ionic flux required for the initiation and conduction of impulses. In addition, this agent increases electrical excitation threshold, reduces rate of rise of action potential and slows nerve impulse propagation thereby causing loss of sensation. |
| Targets&IC50 | 5-HT3:1.7 μM(Kd), nAChR:45.5 μM, Na+ channel:60 μM, NMDAR:0.296 mM |
| In vitro | In anesthetized cats, Procaine (15 mg/kg) enhanced the cellular activity in the ventral hippocampal formation of the amygdala, the ventromedial hypothalamus, the septal nucleus, and the neocortex of the temporal lobe. Procaine acts as a stimulant for marginal system cells. Furthermore, Procaine facilitates the conduction of evoked stimulatory activity from the amygdala to the ventromedial hypothalamus. |
| In vivo | Procaine exhibits the ability to bind to or antagonize nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and the 5-HT(serotonin) receptor-ion channel complex, as well as N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Its primary mechanism of action involves the inhibition of sodium ion influx by affecting the voltage-gated sodium channels on the neuronal cell membranes of peripheral nerves. This disruption of sodium ion flow prevents the generation of action potentials, thereby inhibiting signal transduction. Studies suggest that the receptor sites targeted by procaine are located on the cytoplasmic (internal) portion of the sodium channels. |
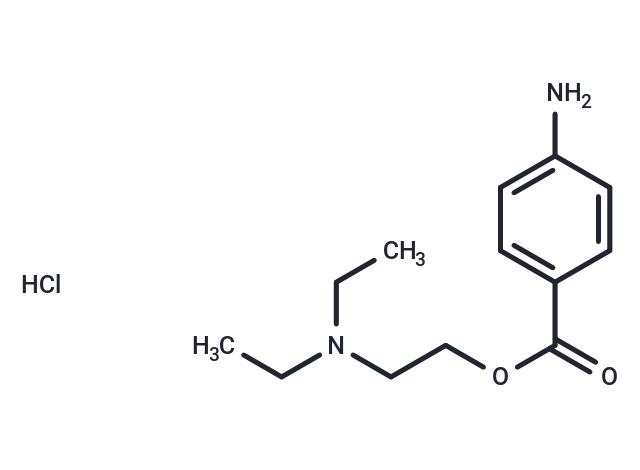
| Alias | Procaine HCl, Novocaine HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 272.77 |
| Formula | C13H20N2O2·HCl |
| Cas No. | 51-05-8 |
| Smiles | Cl.CCN(CC)CCOC(=O)c1ccc(N)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.1761 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 55 mg/mL (201.64 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 50 mg/mL (183.3 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.