Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Bay 59-3074 is a CB1/CB2 receptor partial agonist (Ki: 48.3/45.5 nM). In rat models of chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain, it displays anti-hyperalgesic and antiallodynic properties.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $73 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $119 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $221 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $329 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Bay 59-3074 is a CB1/CB2 receptor partial agonist (Ki: 48.3/45.5 nM). In rat models of chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain, it displays anti-hyperalgesic and antiallodynic properties. |
| Targets&IC50 | CB1:48.3nM(ki), CB2:45.5 nM(ki) |
| In vitro | analgesic, antihyperalgesic, and antiallodynic properties in rat models of acute and chronic pain. The reference concentration is 10 μM. |
| In vivo | In rat models of chronic neuropathic (chronic constriction injury, spared nerve injury, tibial nerve injury, and spinal nerve ligation models) and inflammatory pain (carrageenan and complete Freund's adjuvant models), BAY 59-3074 (0.3-3 mg/kg, p.o.) induced antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects against thermal or mechanical stimuli. Antiallodynic efficacy of BAY 59-3074 (1 mg/kg, p.o.) in the spared nerve injury model was maintained after 2 weeks of daily administration. However, tolerance developed rapidly (within 5 days) for cannabinoid-related side effects, which occur at doses above 1 mg/kg (e.g., hypothermia). Uptitration from 1 to 32 mg/kg p.o. (doubling of daily dose every 4th day) prevented the occurrence of such side effects, whereas antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic efficacy was maintained/increased. No withdrawal symptoms were seen after abrupt withdrawal following 14 daily applications of 1 to 10 mg/kg p.o. |
| Molecular Weight | 453.36 |
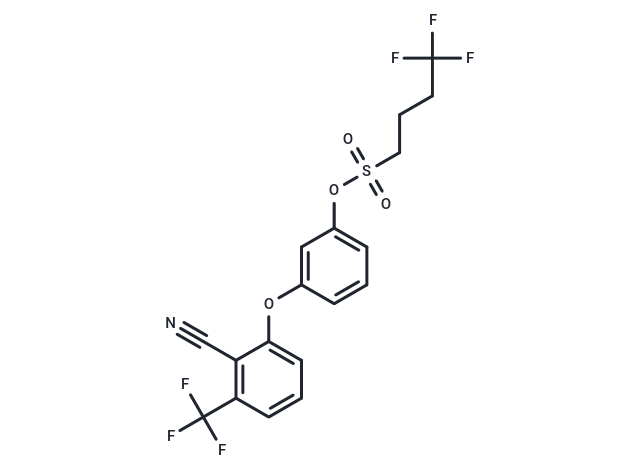
| Formula | C18H13F6NO4S |
| Cas No. | 406205-74-1 |
| Smiles | FC(F)(F)CCCS(=O)(=O)Oc1cccc(Oc2cccc(c2C#N)C(F)(F)F)c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.496g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (110.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.