Shopping Cart
- Remove All
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $157 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $237 | In Stock |
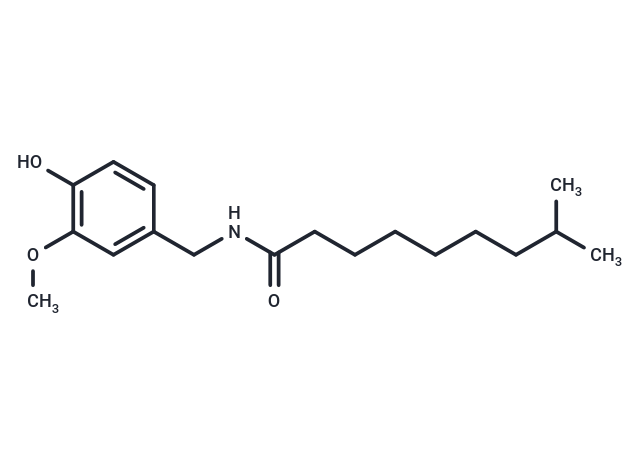
| Description | Dihydrocapsaicin (CCRIS1589) is isolated from Capsicum fruit. Capsaicin is the primary active component of the heat and pain-eliciting lipid soluble fraction of the Capsicum pepper. Like capsaicin, dihydrocapsaicin is an irritant. Capsaicin is found in natural hot pepper extracts along with a number of impurities, including dihydrocapsaicin and several lesser impurities. Separation by HPLC is required in order to obtain pure dihydrocapsaicin. Dihydrocapsaicin represents about 10% of the compound present in commercial preparations purporting to be pure capsaicin, but it has about the same pungency as capsaicin. VR1 (vanilloid receptor 1) is a heat activated calcium ion channel which functions as a part of the normal nociceptive pain pathway. Capsaicin elicits a sensation of burning pain by activation of VR1 on small, non-myelinated polymodal C-type nociceptive nerve fibers. The potency of dihydrocapsaicin at VR1 appears equivalent to capsaicin. Antioxidant. Reduces oxidation of serum lipids. Mutagenic. Dihydrocapsaicin is an activator of VR1. |
| Alias | CCRIS1589, 6,7-Dihydrocapsaicin, 8-Methyl-N-vanillylnonanamide |
| Molecular Weight | 307.43 |
| Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Cas No. | 19408-84-5 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (178.9 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.