Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

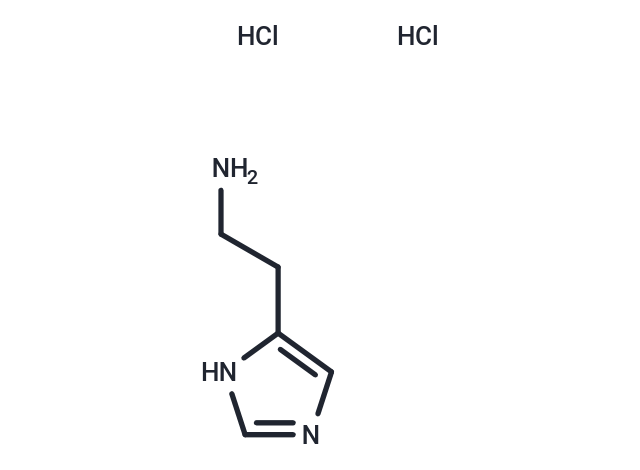
Histamine dihydrochloride (Ceplene) is dihydrochloride form of Histamine. Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound which is a powerful stimulant of gastric secretion, a constrictor of bronchial smooth muscle, a vasodilator, and also a centrally acting neurotransmitter.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $64 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $148 | Backorder | |
| 10 g | $218 | Backorder | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock |
| Description | Histamine dihydrochloride (Ceplene) is dihydrochloride form of Histamine. Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound which is a powerful stimulant of gastric secretion, a constrictor of bronchial smooth muscle, a vasodilator, and also a centrally acting neurotransmitter. |
| In vitro | Histamine suppresses the generation of ROS through the Histaminetype-2 receptor (H2 receptor).[1] Histamine inhibits the generation and release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by monocytes/macrophages (MO) during respiratory burst. Histamine and interleukin-2 (IL-2) act synergistically to activate NK cell cytotoxicity (NKCC). Histamine combined with IL-2 might improve response rates and disease-free survival by protecting the cells of the immune system from oxidative stress and inducing natural endogenous immune cytotoxicity. [2] |
| In vivo | Histamine treatment (0.5 mg/kg or 5.0 mg/kg, twice daily) protects against liver injury as evident by normal serum transaminase levels and significantly reduced liver pathology scores in a rat model with early alcohol-induced liver injury. The protective effect of histamine is blocked by Ranitidine (10 mg/kg), an H2 receptor antagonist, indicating that the histamine effect is predominantly mediated through the H2 receptor. [1] Histamine (30 pg/rat, icv) increases both 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine accumulation and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine acid concentrations in the nucleus accumbens in male rats, and this effect is not affect by H2 antagonist zolantidine, indicating that histamine stimulates mesolimbic DA neurons through an action at the H1 receptor. [3] Histamine (0.5 mg/kg s.c.) reduces the liver tumour weight by 46% and subcutaneous tumour weight by 41% versus rats receiving subcutaneous saline injections. The anti-tumour effect observed by subcutaneous histamine injections is inhibited by Ranitidine (50 mg/kg s.c.) in rats sarcoma. [4] Histamine (1000 mg/kg s.c.) displays acute tissue damage after 24 hours and indications of pathological inflammation at the injection sites at 5 days and 28 days in Sprague-Dawley rats. Histamine (1000 mg/kg s.c.) results in Cmax of 167 mM, tmax of 0.5 hour, t1/2 of 0.95 and AUC of 186 mmol-h/L in male Sprague-Dawley rats. [5] |
| Alias | peremin, Histamine 2HCl, Ceplene |
| Molecular Weight | 184.07 |
| Formula | C5H9N3·2HCl |
| Cas No. | 56-92-8 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.NCCC1=CN=CN1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.14 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 18.4 mg/mL (99.96 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 70 mg/mL (380.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.