Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

N6-Methyladenosine is a methylated adenine residue, glycoside is an endogenous uridine product of transfer RNA degradation. It is the most prevalent internal modification of messenger RNA present in all higher eukaryotes and can modify viral RNA with antiviral activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $66 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $96 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $161 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | N6-Methyladenosine is a methylated adenine residue, glycoside is an endogenous uridine product of transfer RNA degradation. It is the most prevalent internal modification of messenger RNA present in all higher eukaryotes and can modify viral RNA with antiviral activity. |
| In vitro | N6-Methyladenosine is an abundant modification in mRNA and is found within some viruses, and most eukaryotes including mammals, insects, plants and yeast. It is also found in tRNA, rRNA, and small nuclear RNA(snRNA) as well as several long non-coding RNA, such as Xist. [1] [2] [3] N6-Methyladenosine is an endogenous urinary nucleoside product of the degradation of transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA). [4] N6-Methyladenosine is a widespread RNA modification in many tissues with high levels in the brain. N6-Methyladenosine is enriched near stop codons and within 3'UTRs in both mouse and human mRNAs. [5] The recent discovery that FTO, an obesity risk gene, encodes an m6A demethylase implicates m6A as an important regulator of physiological processes. [6] |
| In vivo | LD50: Mice >1 g/kg (i.g.). [7] |
| Kinase Assay | NOD1 Dose Response assay: Day 1 Procedure 1) Harvest HEK-293-T NFKB-Luc at 100% confluency at 100% confluency. 2) Add NOD assay media with Multidrop. 3) Spin down plates at 1000 rpm for 1 min in centrifuge. 4) Serial compound dilutions. 5) Add gamma-tri-DAP to cell suspension at 0.75 ug/mL. 6) Seed 13000 cells/well in 4 uL/well to full plate HEK-293-T NFKB-Luc to TC-treated plate. 7) Spin down plates 500 RPM for 5 min on centrifuge. 8) Lid Plates. Sandwich 4 plates between 2 lidded 384 plates filled with Water. 9) Wrap plates securely in single layer of Plastic Wrap. 10) Incubate overnight (14 hours) in 37 ℃ and 5% CO2 incubator. Day 2 Procedure 1) Add 3 ul/well of SteadyGlo solution with Multidrop. 2) Shake plates on a plate shaker for 20 min. 3) Spin plates 1000 RPM for 1 min using centrifuge. 4) Read luminescence.IC50 values are calculated using GraphPad Prism 5.0.The average Z' for the screen is 0.6, the signal to background is 11.1, signal to noise is 78.6 and signal to window is 6.0. |
| Alias | NSC-29409, N-Methyladenosine, m6A, 6-Methyladenosine |
| Molecular Weight | 281.27 |
| Formula | C11H15N5O4 |
| Cas No. | 1867-73-8 |
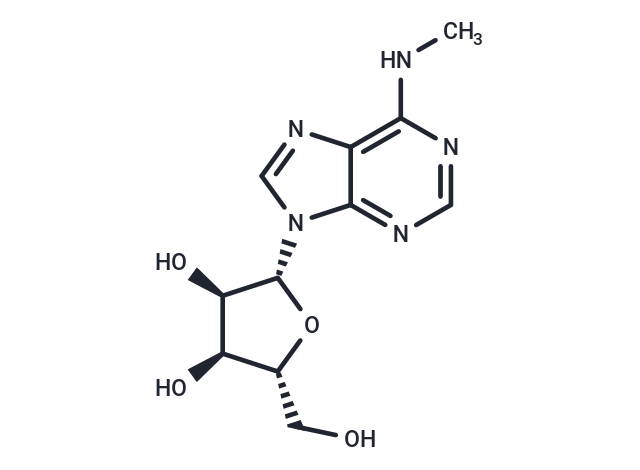
| Smiles | O[C@H]1[C@H](N2C=3C(N=C2)=C(NC)N=CN3)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.85g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (7.11 mM) DMSO: 50 mg/mL (177.77 mM) H2O: 14 mg/mL (49.77 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/H2O/DMSO
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.