Shopping Cart
- Remove All
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $112 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $209 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $377 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $579 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $71 | In Stock |
| Description | NMS-873 is a potent and selective allosteric inhibitor of VCP/p97. |
| In vivo | NMS-873 activates the unfolded protein response, disrupts autophagy, and induces cell death. Across various blood and solid tumor cell lines, it inhibits the sensitivity of p97 to protease digestion, preventing the degradation of the linker-D2 domain, thereby exhibiting antiproliferative activity. |
| Kinase Assay | Biochemical assay development and HTS: The ATPase activity and the kinetic parameters of recombinant wild-type VCP and its mutants are evaluated by monitoring ADP formation in the reaction, using a modified NADH-coupled assay. As ADP and NADH are ATP-competitive inhibitors of VCP ATPase activity, the standard protocol for the NADH-coupled assay is modified into a two-step procedure. In the first part, an ATP-regenerating system (40 U/ml pyruvate kinase and 3 mM phosphoenolpyruvate) recycles the ADP produced by VCP activity, keeps the substrate concentration constant (thus preventing product inhibition) and accumulates a stoichiometric amount of pyruvate. In the second part, the VCP enzymatic reaction is quenched with 30 mM EDTA and 250 μM NADH and stoichiometrically oxidized by 40 U/ml lactic dehydrogenase to reduce accumulated pyruvate. The decrease of NADH concentration is measured at 340 nm using a Tecan Safire 2 reader plate. The assay is performed in 96- or 384-well UV plates in a reaction buffer with 50 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 0.2 mg/mL BSA, 10 mM MgCl2 and 2 mM DTT. Experimental data are fitted with a cooperative equation obtaining a Ks* of about 60 μM and a Hill coefficient (n) of 2.0 ± 0.1. The HTS campaign is performed against a 1-million-compound library using a miniaturized assay in 1,536-well format and a more sensitive ADP detection system, Transcreener ADP FP. A 20-min preincubation of 10 nM VCP and 10 μM inhibitor is performed, after which 10 μM ATP is added to the reaction, which is allowed to proceed for 90 min before quenching. The average Z′ of the screening is 0.58, and the hit rate using 3× s.d. (38% inhibition) as cutoff is 1.7%. Primary hits with >60% inhibition at 10-μM concentration are pruned using physicochemical and structural filters to leave 7,516 compounds.At the end, reconfirmation is performed in duplicate on 3,988 primary hits, and 500 compounds are selected for a dose-response evaluation using the previously described NADH-modified coupled assay. The potency of the most interesting HTS hits is measured against both wild-type VCP and the C522T mutant. ATP concentrations that yielded the half-maximal velocity (Ks*) for each enzyme, corresponding to 60 μM and 130 μM for the wild type and C522T mutant, respectively, are used in the assay. To explore the dependency of reversible inhibitors from substrate concentration, their potency is evaluated also at saturating ATP concentration (1 mM) and compared to the potency of a standard ATP competitive inhibitor (AMP-PNP). |
| Cell Research | Cells are seeded at 1,600 cells per well in 384-well white clear-bottom plates. Twenty-four hours after seeding, cells are treated with the compounds (eight dilution points, in duplicate, for each compound) and incubated for an additional 72 h at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Cells are then lysed, and the ATP content in each well is determined using a thermostable firefly luciferase–based assay as a measure of cell viability. IC50 values are calculated using the percentage of growth of treated cells versus the untreated control. (Only for Reference) |
| Molecular Weight | 520.67 |
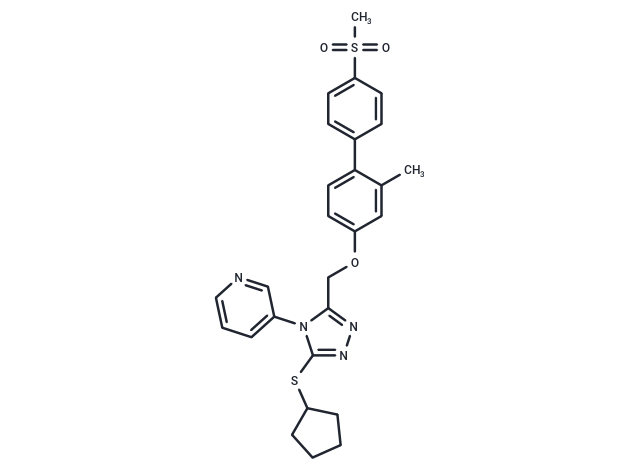
| Formula | C27H28N4O3S2 |
| Cas No. | 1418013-75-8 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (115.24 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.