Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

OAC2 is an Oct4 activator which activates expression through the Oct4 gene promoter; enhances reprogramming efficiency by increasing the rate of production of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from embryonic fibroblasts; an analog of OAC1.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $63 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $128 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $233 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $368 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $546 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $57 | In Stock |
| Description | OAC2 is an Oct4 activator which activates expression through the Oct4 gene promoter; enhances reprogramming efficiency by increasing the rate of production of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from embryonic fibroblasts; an analog of OAC1. |
| In vitro | Octamer-binding transcription factor 4 (Oct4) is crucial for initiating and maintaining cellular pluripotency, especially during early differentiation stages, and cannot be substituted by any family members for this function[1]. Essential for embryonic stem cell (ESC) pluripotency and reprogramming, Oct4, along with Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc, benefits from the structural analog OAC2, which activates Oct4 and Nanog reporters like OAC1. OAC1 and its analogs OAC2 and OAC3 significantly enhance reprogramming efficiency by up to 2.75% and accelerate iPSC colony formation by 3 to 4 days[2]. |
| Cell Research | The Oct4-luc or Nanog-luc cells are treated with compound OAC1 or its structural analogs OAC2, OAC3 at 1 μM concentration or at indicated concentrations. Other compounds used include 2 μM BIO, 2 μM BIX, 2 μM 5'-azacytidine, 25 μg/mL Vitamin C, 10 nM Am580, 5 μM tranylcypromine, and 0.5 mM valporic acid. Luciferase reporter assays are performed 24 h after compound treatment or at indicated time points. For Topflash reporter assays, 0.2 μg β-catenin–responsive Topflash reporter gene plasmid is introduced into CV1 cells using trasfection. Compounds are added 6 h after transfection. Luciferase activity is measured 48 h after compound treatment using the Glo Luciferase Assay System[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 236.27 |
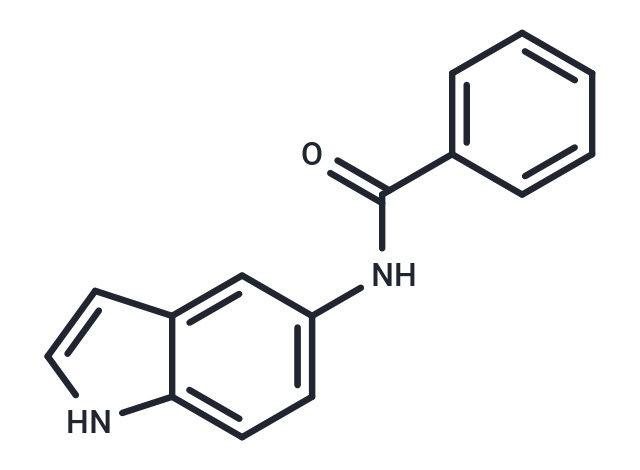
| Formula | C15H12N2O |
| Cas No. | 6019-39-2 |
| Smiles | O=C(Nc1ccc2[nH]ccc2c1)c1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.307 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 23.6 mg/mL (99.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.