Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Saikosaponin A has a variety of pharmacological benefits, including antiepileptic, anti-osteoporosis, antioxidant, anti-in ammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-bacterial activities. It can effectively attenuate neuropathic pain in CCI rats by inhibiting the activation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in spinal cord. It can inhibit NMDA receptor current and persistent sodium current, and inhibit the TNF-α level, the IL-1β production, and cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase)-1 activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $126 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $247 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $409 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $596 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $115 | In Stock |
| Description | Saikosaponin A has a variety of pharmacological benefits, including antiepileptic, anti-osteoporosis, antioxidant, anti-in ammatory, immunomodulatory, and anti-bacterial activities. It can effectively attenuate neuropathic pain in CCI rats by inhibiting the activation of p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in spinal cord. It can inhibit NMDA receptor current and persistent sodium current, and inhibit the TNF-α level, the IL-1β production, and cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase)-1 activity. |
| Molecular Weight | 780.98 |
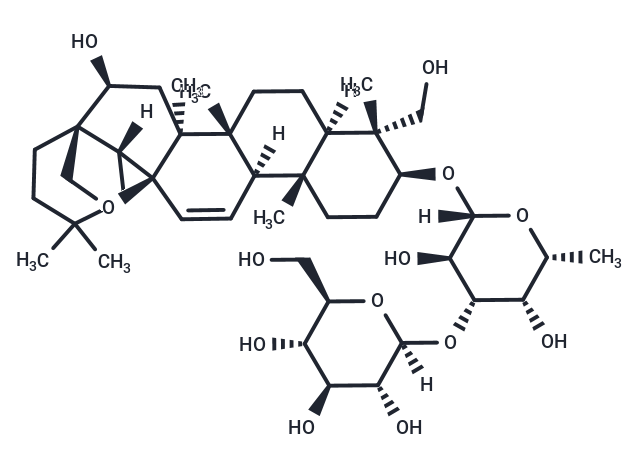
| Formula | C42H68O13 |
| Cas No. | 20736-09-8 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12CC(C)(C)CC[C@@]11CO[C@@]22C=C[C@]3([H])[C@@]4(C)CC[C@H](O[C@]5([H])O[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](O[C@]6([H])O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]6O)[C@H]5O)[C@@](C)(CO)[C@]4([H])CC[C@@]3(C)[C@]2(C)C[C@@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.36 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (64.02 mM) Ethanol: 30 mg/mL H2O: Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.