Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

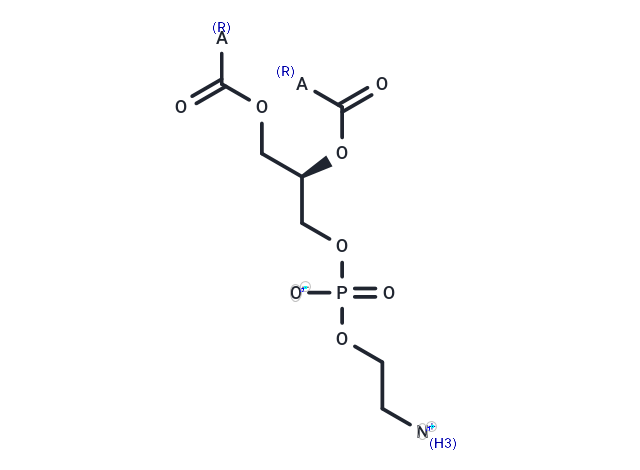
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) contains phospholipids found in mammals, formed by decarboxylation of phosphatidylserine.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $233 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $545 | 35 days | |
| 50 mg | $987 | 35 days |
| Description | Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) contains phospholipids found in mammals, formed by decarboxylation of phosphatidylserine. |
| In vitro | Phosphatidylethanolamine (0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1 mmol/L) processing HeLa, Results show that the Phosphatidylethanolamine on cell growth inhibitory effect was dose and time dependent, and induce cell apoptosis, but does not affect the cell cycle. [1] |
| Alias | PE, LPI |
| Formula | N/A |
| Cas No. | 97281-51-1 |
| Smiles | [R]C(OC[C@@H](OC([R])=O)COP([O-])(OCC[NH3+])=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Solubility Information | Chloroform: 4 mg/mL, Sonication is recommended. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.