Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

ACHP Hydrochloride (IKK-2 Inhibitor VIII) is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of IKK-β with an IC50 of 8.5 nM.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $147 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $239 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $395 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $569 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $818 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,630 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $162 | In Stock |
| Description | ACHP Hydrochloride (IKK-2 Inhibitor VIII) is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of IKK-β with an IC50 of 8.5 nM. |
| Targets&IC50 | IKKβ:8.5 nM, IKKα:250 nM |
| In vitro | ACHP Hydrochloride (Compound 4j) exhibits potent IKK-β inhibitory (IC50: 8.5 nM) and cellular activities (IC50: 40 nM, in A549 cells), moderately inhibits IKK-α (IC50: 250 nM), and demonstrates selectivity against other kinases such as IKK3, Syk, and MKK4 (IC50>20,000 nM). It inhibits NF-κB-dependent reporter gene activation in TNFα-activated HEK293 cells and PMA/calcium ionophore-activated Jurkat T cells but does not inhibit PMA-induced AP-1 activation in MRC-5 cells or PMA/calcium ionophore-induced NF-κB-dependent reporter gene transcription in Jurkat cells even at concentrations exceeding 10 μM. ACHP selectively interferes with the NF-κB signaling cascade by inhibiting IKK-β in living cells and inhibits their growth dose-dependently. Tax-active cell lines are more susceptible to ACHP than Tax-inactive cell lines and Jurkat (IC50 values in Tax-active cell lines, Tax-inactive cell lines, or Jurkat are 3.1±1.3 μM, 10.7±1.7 μM, and 23.6 μM, respectively), suggesting that the growth of Tax-active cells depends on NF-κB more than Tax-inactive cells [1][2]. |
| In vivo | ACHP is orally bioavailable in mice (BA: 16%) and rats (BA: 60%), with significant in vivo activity in anti-inflammatory models (arachidonic acid-induced mouse ear edema model). It has reasonable aqueous solubility (0.12 mg/mL in pH 7.4 isotonic buffer), excellent Caco-2 permeability (Papp 62.3×10^-7 cm/s), and low clearance in rats (0.33 L/h/kg). In an acute inflammation model, ACHP demonstrates oral efficacy at 1 mg/kg in a dose-dependent manner [1]. |
| Cell Research | HTLV-1-infected T-cell lines, ATL-35T, 81-66/45, MJ, and MT-2 cells, human ATL cell lines established from ATL patients, ATL-102, ED-40515(?) and TL-Om1 cells, and an HTLV-1-negative T-cell leukemia cell line Jurkat are used in this study. Approximately 1.5×10^4 cells are cultured in 96-well plates in triplicates at 37°C. Growth inhibitory effect of ACHP (0.01, 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 50 and 100 μM) is determined using MTT assay. Optical densities (OD) at 570 and 630?nm are measured with a multi-plate reader. Cell viability (%) is calculated [2]. |
| Animal Research | In vivo arachidonic acid-induced ear edema in mice: ear edema is induced by topical application of arachidonic acid (500 μg/ear). ACHP (0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg, p.o.), Dexamethasone, and vehicle (10% cremophor in saline) are given po 60 min before the arachidonic acid application. Ear thickness is measured at 0, 1, 3, and 6 h after the arachidonic acid application [1]. |
| Alias | IKK-2 Inhibitor VIII |
| Molecular Weight | 400.9 |
| Formula | C21H25ClN4O2 |
| Cas No. | 406209-26-5 |
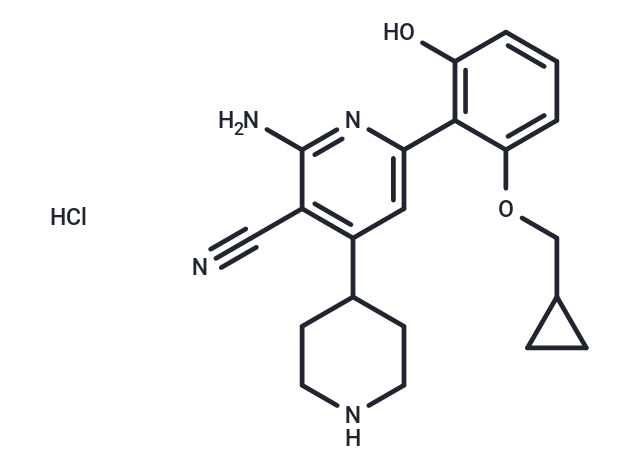
| Smiles | Cl.Nc1nc(cc(C2CCNCC2)c1C#N)-c1c(O)cccc1OCC1CC1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (112.25 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.