Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Ko 143 is a selective inhibitor of ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2; BCRP).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $113 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $228 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $413 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $745 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $66 | In Stock |
| Description | Ko 143 is a selective inhibitor of ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2; BCRP). |
| Targets&IC50 | ABCG2:26 nM (EC50) |
| In vitro | In HEK G2 cells and mouse G2 cells, Ko143 (10 nM) significantly decreases the IC50 of MTX. Ko143 (1-100 μM) metabolite does not inhibit the function of ABC transporters [1]. Reversal of drug resistance in SKF 104864A-selected mouse MEF3.8/T6400 cells and human IGROV1/T8 cells by Ko143 [2]. Ko143 inhibits BCRP-mediated transport of ZD 4522 in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) 2-BCRP421CC (wild type) cells and MDCK2-BCRP421AA (mutant type) cells [3]. |
| In vivo | Ko143 (10 mg/kg, p.o.) increases the oral availability of SKF 104864A in mice [2]. |
| Cell Research | Cells are plated at 400 or 1000/well in 96-well plates the night before the addition of drugs. A concentration series of the drug is applied along one plate axis and left for the duration of the assay. Plates are harvested after 4-5 days while untreated wells are still subconfluent. Relative cell proliferation is quantified with CyQuant or Sybr Green I fluorescent nucleic acid stains. Assays with human cell lines are performed in the presence of 0.1 μm PSC833 to inhibit confounding P-gp activity [2]. |
| Animal Research | Oral toxicity of FTC analogs in mice is tested by mixing 50 mg/mL stocks in DMSO 1:1 with Tween 80 (polyoxyethylene sorbitan mono-oleate) and diluting with 5% w/v glucose such that the final volume administered by oral gavage is 10 μL/g of body weight. Pairs of mice are administered oral doses of 50 mg/kg Ko132, Ko134, Ko143, or vehicle under light methoxyflurane anesthesia. Final tests of 50 mg/kg Ko134 or Ko143 are performed on additional pairs of unanesthetized animals to observe any behavioral effects. Further, another pair of mice receive a higher dose of 100 mg/kg Ko134. For i.p. toxicity tests, the FTC analog stocks in DMSO are dispersed in at least 10 volumes of sterile corn oil such that the injected volume is 5 μL/g of body weight. After pilot tests at lower doses show no adverse effects, mice (4 per group) are administered vehicle or 10 mg/kg i.p. of Ko132, Ko134, or Ko143. The mice are observed continuously during the first hour after administration and then at increasing intervals for 2 weeks, after which they are sacrificed for histological examination of major organs and structures [2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 469.57 |
| Formula | C26H35N3O5 |
| Cas No. | 461054-93-3 |
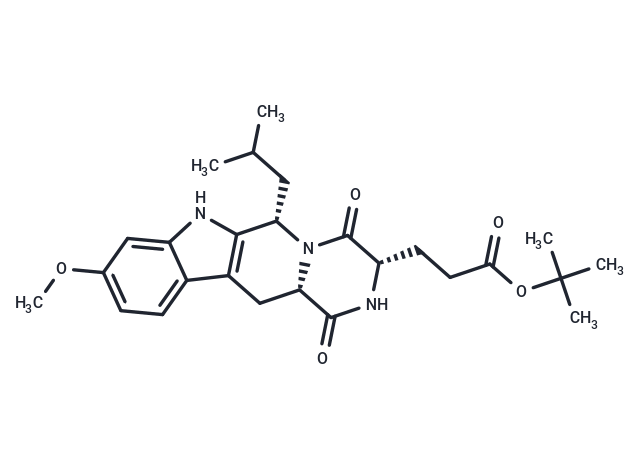
| Smiles | COc1ccc2c3C[C@@H]4N([C@@H](CC(C)C)c3[nH]c2c1)C(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)NC4=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.24 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 90 mg/mL (191.66 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.