Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Trovafloxacin, a broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic, exhibits potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria.
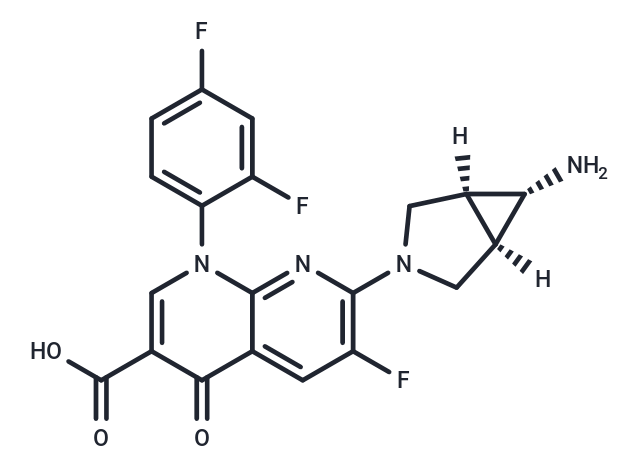

| Description | Trovafloxacin, a broad-spectrum quinolone antibiotic, exhibits potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria. |
| Targets&IC50 | PANX1:4 μM (IC50) |
| In vitro | In HepG2 cells, Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; ) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 4 ng/mL) incubation induces apoptosis and increases leakage of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)[1]. Trovafloxacin (20 μM; 24 hours; HepG2 cells) and TNF (4 ng/mL) incubation increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα[1]. Trovafloxacin prolongs TNF-induced activation of MAPKs and IKKα/β activation in HepG2[1]. Trovafloxacin is a potent TO-PRO-3 uptake inhibitor by apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin also inhibits ATP release from apoptotic cells. Trovafloxacin is equally active against both penicillin-susceptible and -resistant pneumococci, with MICs of 0.06-0.25 mg/mL reported for more than 700 isolates. The MICs of Trovafloxacin at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for 55 isolates of pneumococci is 0.125 μg/mL[3]. |
| In vivo | In male C57BL/6 J mice, TNF-induced p65 nuclear translocation disrupted by Trovafloxacin (150 mg/kg; oral administration). Trovafloxacin treatment increases expression of early NF-κB-related factors A20 and IκBα[1]. Trovafloxacin increased serum levels of alanine amino transferases (ALT) and pro-inflammatory cytokines when administered in combination with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or TNF to mice induces severe liver toxicity associated with vast apoptotic areas in the liver[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 416.35 |
| Formula | C20H15F3N4O3 |
| Cas No. | 147059-72-1 |
| Smiles | O=C(C1=CN(C2=CC=C(F)C=C2F)C3=NC(N4C[C@@]5([H])[C@H](N)[C@@]5([H])C4)=C(F)C=C3C1=O)O |
| Relative Density. | 1.612 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 4.16 mg/ml (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.