Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

VE-821 (ATR Inhibitor IV) is a selective ATP competitive inhibitor of ATR( Ki/IC50: 13/26 nM in cell-free assays).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $126 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $51 | In Stock |
| Description | VE-821 (ATR Inhibitor IV) is a selective ATP competitive inhibitor of ATR( Ki/IC50: 13/26 nM in cell-free assays). |
| Targets&IC50 | ATR:13 nM (Ki, cell free) |
| In vitro | VE-821 exhibits high selectivity for ATR with minimal cross-reactivity against related PIKKs, including ATM, DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), mammalian target of rapamycin, and phosphoinositol 3-kinase-γ (Kis of 16 μM, 2.2 μM, >1 μM and 3.9 μM, respectively). It inhibits H2AX phosphorylation in hydroxyurea-treated HT29 cancer cells without affecting M059J or HT144 lines treated with neocarzinostatin [1]. VE-821 significantly increases the sensitivity of PSN-1, MiaPaCa-2, and primary PancM pancreatic cancer cells to radiation and gemcitabine under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions, leading to the inhibition of radiation-induced G2/M arrest [2]. Additionally, VE-821 (1 and 4 μM) enhances H2AX phosphorylation at Ser139 in OVCAR-8 cells induced by topotecan and cisplatin but does not block ATR-mediated Ser345 Chk1 or Ser296 autophosphorylation induced by gemcitabine, topotecan, or cisplatin [3]. |
| Kinase Assay | The ability of compounds (e.g., VE-821) to inhibit ATR, ATM or DNAPK kinase activity is tested using a radiometric-phosphate incorporation assay. A stock solution is prepared consisting of the appropriate buffer, kinase, and target peptide. To this is added the compound of interest, at varying concentrations in DMSO to a final DMSO concentration of 7%. Assays are initiated by addition of an appropriate [g-33P]ATP solution and incubated at 25°C. Assays are stopped, after the desired time course, by addition of phosphoric acid and ATP to a final concentration of 100 mM and 0.66 μM, respectively. Peptides are captured on a phosphocellulose membrane, prepared, and washed six times with 200 μL of 100 mM phosphoric acid, prior to the addition of 100 μL of scintillation cocktail and scintillation counting on a 1450 Microbeta Liquid Scintillation Counter. Dose-response data are analyzed using GraphPad Prism software [4]. |
| Cell Research | Clonogenic survival assays were performed as described before. Briefly, logarithmically growing cells were plated in triplicate in 6-well tissue culture dishes under oxic (21% O2) or hypoxic conditions (0.5% O2) using an InVivo2 300 chamber. Cells were incubated for 6 h before irradiation under oxia or hypoxia using tightly sealed chambers. The target O2 level was achieved within 6 h of gassing and maintained during irradiation, as confirmed by an OxyLite oxygen probe. Cells irradiated under hypoxia were exposed to normoxia at 1 h post-irradiation. As standard, VE-821 (1 μM) was added 1 h prior to irradiation (6 Gy) and was washed away 72 h after irradiation. For the chemotherapy experiments, cells were initially exposed to increasing concentrations of gemcitabine (5, 10 and 20 nM) for 24 h before addition of the VE-821 (1 μM) for another 72 h. The effect of triple combination of irradiation with VE-821 and gemcitabine was examined as well. Cells were incubated for 10–21 d until colonies were stained with 0.5% crystal violet and counted in a CellCount automated colony counter. Clonogenic survival was calculated and data were fitted in GraphPad Prism 4.0 [2]. |
| Alias | ATR Inhibitor IV |
| Molecular Weight | 368.41 |
| Formula | C18H16N4O3S |
| Cas No. | 1232410-49-9 |
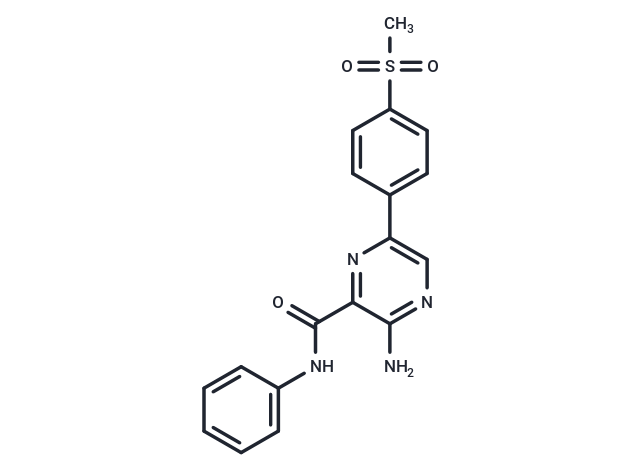
| Smiles | CS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(cc1)-c1cnc(N)c(n1)C(=O)Nc1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.394 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 69 mg/mL (187.29 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.