Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

6-Hydroxy-DOPA is an allosteric inhibitor of RAD52, it inhibits proliferation of BRCA-deficient cancer cells in vitro and also inhibits APE1.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | 42 € | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | 100 € | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | 160 € | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | 325 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 520 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 784 € | In Stock |
| Description | 6-Hydroxy-DOPA is an allosteric inhibitor of RAD52, it inhibits proliferation of BRCA-deficient cancer cells in vitro and also inhibits APE1. |
| In vitro | We identify the small molecule 6-hydroxy-DL-dopa (6-OH-dopa) as a major allosteric inhibitor of the RAD52 ssDNA binding domain. For example, we find that multiple small molecules bind to and completely transform RAD52 undecamer rings into dimers, which abolishes the ssDNA binding channel observed in crystal structures. 6-OH-Dopa also disrupts RAD52 heptamer and undecamer ring superstructures, and suppresses RAD52 recruitment and recombination activity in cells with negligible effects on other double-strand break repair pathways. |
| In vivo | Importantly, we show that 6-OH-dopa selectively inhibits the proliferation of BRCA-deficient cancer cells, including those obtained from leukemia patients. Taken together, these data demonstrate small-molecule disruption of RAD52 rings as a promising mechanism for precision medicine in BRCA-deficient cancers. |
| Alias | 6-Hydroxy-DL-DOPA |
| Molecular Weight | 213.19 |
| Formula | C9H11NO5 |
| Cas No. | 21373-30-8 |
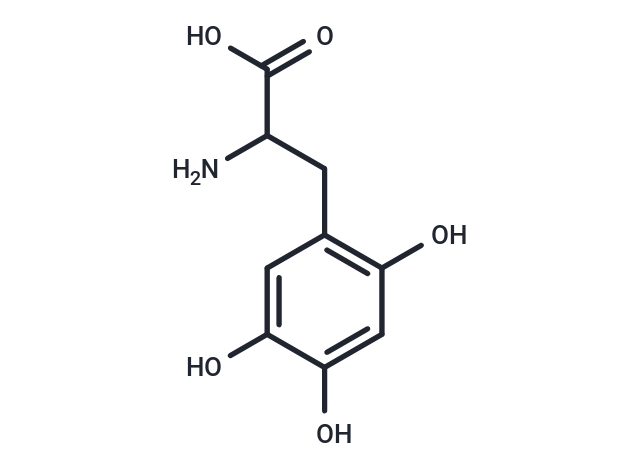
| Smiles | C(C(C(O)=O)N)C1=C(O)C=C(O)C(O)=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.606 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 2.13 mg/mL (9.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.