Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Acarbose (BAY g 5421) is an inhibitor of α-Glucosidases with antihyperglycemic activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $79 | In Stock |
| Description | Acarbose (BAY g 5421) is an inhibitor of α-Glucosidases with antihyperglycemic activity. |
| In vitro | Acarbose binds to and inhibits α-glucosidase, an enteric enzyme found in the brush border of the small intestines that hydrolyzes oligosaccharides and disaccharides into glucose and other monosaccharides. In addition, acarbose inhibits pancreatic α-amylase which hydrolyzes complex starches to oligosaccharides in the small intestines. |
| Cell Research | Cell viability is determined using the MTT assay. Cells are seeded in 24-well culture plates at a density of 2×104 cells/well, incubated for 48 h, treated with acarbose at varying concentrations (0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 5.0 μM) for 24 h; or pre-treated with TNF-α (20 ng/mL) for either 24 h or 48 h to evaluate the dose-dependent effects of acarbose on VSMC growth and viability, cultured with 0.5 mg/mL MTT at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 for another 4 h, and solubilized with isopropanol. The viable cell number varies directly with the concentration of formazan product measured spectrophotometrically at 563 nm. |
| Alias | BAY g 5421 |
| Molecular Weight | 645.6 |
| Formula | C25H43NO18 |
| Cas No. | 56180-94-0 |
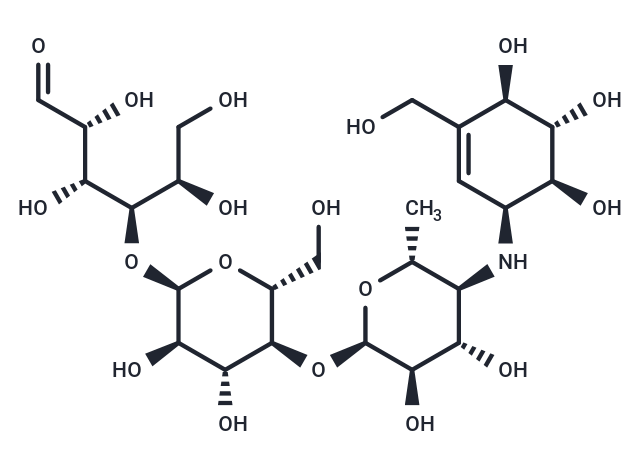
| Smiles | O([C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C=O)O)O)[C@@H](CO)O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O)[C@@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](N[C@H]3C=C(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]3O)[C@@H](C)O2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.4278 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (77.45 mM) H2O: 64.5 mg/mL (100 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.