Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BAR501 is an effective and specific GPBAR1 agonist (EC50: 1 μM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $44 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $163 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $320 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $120 | In Stock |
| Description | BAR501 is an effective and specific GPBAR1 agonist (EC50: 1 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | GPBAR1:1 μM(EC50) |
| In vitro | In HEK293 cells overexpressing a CRE along with GPBAR1, BAR501 effectively transactivates GPBAR1 (EC50: 1 μM). In GLUTAg cells, BAR501 (10 μM) increases the mRNA expression of GLP-1 by 2.5 folds. |
| In vivo | Pretreating rats for 6 days with BAR501 (15 mg/kg) reduces basal portal pressure and blunts the vasoconstriction activity of norepinephrine. BAR501 attenuates hepatic vasomotor activity induced by methoxamine and shear stress and exerts direct vasodilatory activity in the CCl4 model. BAR501 (15 mg/kg) also reduces AST plasma levels and portal pressure, and it attenuates endothelial dysfunction by regulating CSE expression/activity. |
| Cell Research | For GPBAR1 mediated transactivation, HEK-293T cells are plated at 10000 cells/well in a 24 well-plate and transfected with 200 ng of pGL4.29, a reporter vector containing a cAMP response element (CRE) that drives the transcription of the luciferase reporter gene luc2P, with 100 ng of pCMVSPORT6-human GPBAR1, and with 100 ng of pGL4.70. At 24 h post-transfection, HepG2 and HEK293T cells are incubated with 10 μM BAR501 for 18 h and luciferase activities are assayed and normalized against the Renilla activities[1]. |
| Animal Research | Animal: C57BL6 miceAdministration: i.p., 500 μL/kg of CCl4 in an equal volume of paraffin oil twice a week for 9 weeks. CCL4 mice are randomized to receive BAR501 (15 mg/Kg daily by gavage) or vehicle (distilled water). Serum bilirubin, albumin, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase are measured by routine biochemical clinical chemistry[1]. |
| Alias | BAR 501 |
| Molecular Weight | 406.64 |
| Formula | C26H46O3 |
| Cas No. | 1632118-69-4 |
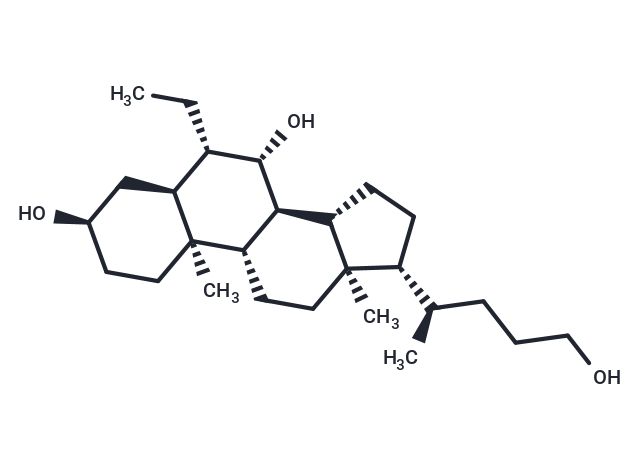
| Smiles | CC[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCO)[C@@]3(C)CC[C@@H]2[C@@]2(C)CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H]12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.047 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (122.96 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.