Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

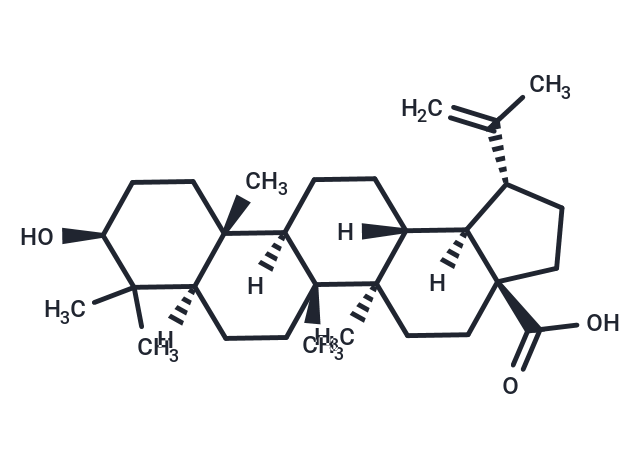
Betulinic acid (ALS-357) is a pentacyclic lupane-type triterpene derivative of betulin (isolated from the bark of Betula alba, the common white birch) which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $174 | In Stock |
| Description | Betulinic acid (ALS-357) is a pentacyclic lupane-type triterpene derivative of betulin (isolated from the bark of Betula alba, the common white birch) which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. |
| Targets&IC50 | HIV-1:1.4 μM(EC50), Aminopeptidase N:7.3 μM, Topo I (eukaryotic):5 μM |
| In vitro | In LNCaP cell cultures of athymic nude mice, Betulinic acid inhibits the growth of prostate cancer cells and tumors (xenografts). This inhibitory effect is partly due to the downregulation of protease-dependent Sp1/3/4 and several SP-regulated genes. |
| In vivo | As an anti-melanoma agent, Betulinic acid inhibits the activity of aminopeptidase N (IC50: 7.3 μM). It exhibits anti-HIV properties by blocking HIV replication in H9 lymphocytes (EC50: 1.4 μM) and inhibiting the growth of uninfected H9 cells (IC50: 13 μM). Moreover, Betulinic acid shows potential as an anti-cancer candidate, suppressing the activity of eukaryotic topoisomerase I (IC50: 5 μM). |
| Kinase Assay | Topoisomerase I-DNA interaction: Annealed 25-mer duplex of oligonucleotide-1 and oligonicleotide-2 is incubated with 25 or 50 units of rat liver topoisomerase I at 8 °C for 15 min in the presence or absence of betulinic acid in binding buffer. After incubation the reaction mixtures are electrophoresed in 7% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel at 4 °C in 0.167 × TBE buffer and DNA bands are stained with ethidium bromid |
| Alias | Lupatic acid, Betulic acid, ALS-357 |
| Molecular Weight | 456.7 |
| Formula | C30H48O3 |
| Cas No. | 472-15-1 |
| Smiles | C(O)(=O)[C@]12[C@@]([C@@]3([C@@](C)(CC1)[C@@]4(C)[C@](CC3)([C@]5(C)[C@@](CC4)(C(C)(C)[C@@H](O)CC5)[H])[H])[H])([C@H](C(C)=C)CC2)[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.065 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 10 mg/mL (21.9 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 33.3 mg/mL (72.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.