Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

NM107 (2'-C-Methylcytidine) is a ribonucleoside with broad-spectrum antiviral activity and acts as a nucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, demonstrating an EC50 of 1.85 μM in wild-type replicon cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $57 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $77 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $119 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $157 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $196 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $62 | In Stock |
| Description | NM107 (2'-C-Methylcytidine) is a ribonucleoside with broad-spectrum antiviral activity and acts as a nucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase, demonstrating an EC50 of 1.85 μM in wild-type replicon cells. |
| In vitro | NM107 reduces the number of viral plaques in BHK-21 cells infected with dengue type 2, reovirus type 1, West Nile, and yellow fever RNA viruses with EC50 values of 95, 26, 80, and 75 μM, respectively. NM107 inhibits hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication (EC50 = 2.2 μM in a replicon assay) and protects MDBK cells from infection with bovine virus diarrhea virus (BVDV; EC50 = 2.2 μM) and human corona virus (HCoV; EC50 = 90 μM). It also reduces infectious virus yield in BHK-21 cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV; EC50 = 6.4 μM) and swine vesicular disease virus (SVDV; EC50 = 45.2 μM)[1]. |
| In vivo | Prolonged norovirus shedding may occur in certain patients, such as organ transplant recipients. Established a mouse model for persistent norovirus infection (using the mouse norovirus MNV.CR6 strain). The nucleoside viral polymerase inhibitor 2′-C-methylcytidine (2CMC), but not favipiravir (T-705), reduced viral shedding to undetectable levels. Viral rebound was observed after stopping treatment, which was again effectively controlled by treatment with 2CMC. No drug-resistant variants emerged[2]. |
| Animal Research | For all experiments, age- and sex-matched mice 8 to 12 weeks of age were infected by oral gavage with 10^6 CCID50 (50% cell culture infective doses) of CR6. At 7 days postinfection (p.i.), mice were left untreated (n = 9) or were treated with 100 mg/kg daily of 2'-C-Methylcytidine(2CMC) subcutaneously for 5 (n = 4), 7 (n = 4), or 11 (n = 4) days. Two more rounds of a 14-day treatment (with an ~4-week interval in between) with 2CMC (n = 10) or favipiravir (200 mg/kg daily by oral gavage [n = 5]) were given. On each day after infection, the general condition and weight of treated and untreated mice were assessed, individual stool samples were collected (whenever possible during one daily period of observation), and levels of MNV RNA were quantified by reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)[2]. |
| Alias | NM-107, 2'-C-Methylcytidine |
| Molecular Weight | 257.24 |
| Formula | C10H15N3O5 |
| Cas No. | 20724-73-6 |
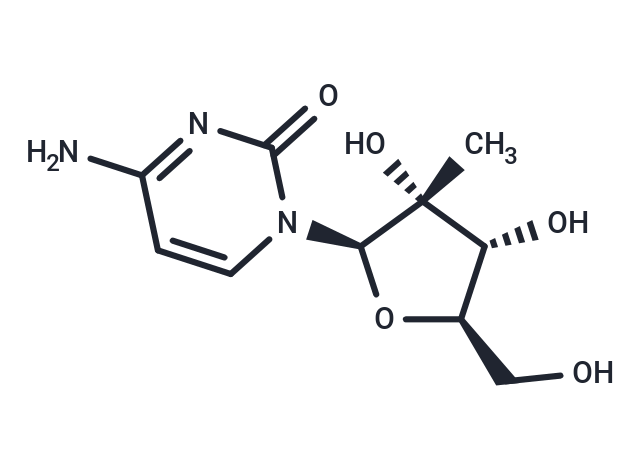
| Smiles | C[C@@]1(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1n1ccc(N)nc1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.72g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 50 mg/mL (194.37 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.