Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

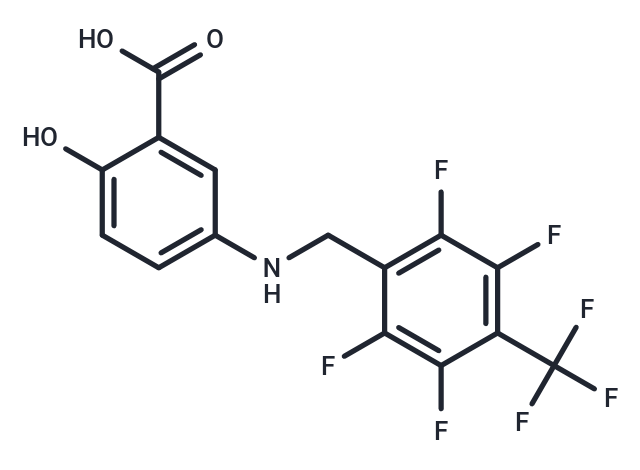
Nelonemdaz (Neu2000) is an NMDA receptor antagonist with antioxidant activity and neuroprotective activity used in the study of cerebral infarction reperfusion injury and acute ischemic stroke.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $372 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $689 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $987 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,530 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $2,970 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $173 | In Stock |
| Description | Nelonemdaz (Neu2000) is an NMDA receptor antagonist with antioxidant activity and neuroprotective activity used in the study of cerebral infarction reperfusion injury and acute ischemic stroke. |
| In vitro | Nelonemdaz (0.19-12.5 μM) dose-dependently reduces the amount of reactive oxygen species/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) formation induced by Antimycin A and inhibits the formation of malondialdehyde (MDA)[3]. |
| In vivo | In male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 260 to 300 g (subjected to the clip occlusion model), Nelonemdaz (0.5-20 mg/kg; intravenous administration 5 minutes after reperfusion) exhibited significant neuroprotective effects[1]. |
| Alias | Salfaprodil free base, Neu2000 |
| Molecular Weight | 383.22 |
| Formula | C15H8F7NO3 |
| Cas No. | 640290-67-1 |
| Smiles | OC(=O)c1cc(NCc2c(F)c(F)c(c(F)c2F)C(F)(F)F)ccc1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.659 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (260.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.