Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

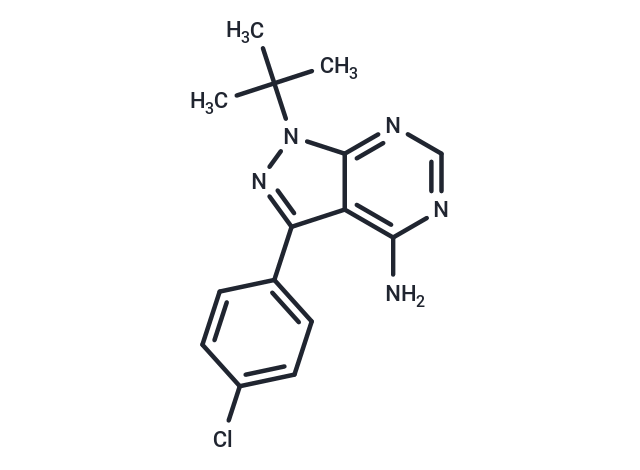
PP2 (AG 1879,AGL 1879) is a effective inhibitor of Lck/Fyn (IC50:4/5 nM) , ~100-fold less potent to EGFR, inactive for ZAP-70, PKA and JAK2.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $63 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $118 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $338 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $536 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $763 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $68 | In Stock |
| Description | PP2 (AG 1879,AGL 1879) is a effective inhibitor of Lck/Fyn (IC50:4/5 nM) , ~100-fold less potent to EGFR, inactive for ZAP-70, PKA and JAK2. |
| Targets&IC50 | Lck:4 nM, Fyn:5 nM |
| In vitro | In rats with focal cerebral ischemic damage, PP2 reduces the infarct area by approximately 50%. Compared to the control group, PP2 (1.5 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly improves neurological function scores in rats with this condition. Additionally, in SCID mice implanted with HT29 cells in the spleen, PP2 (5 mg/kg/day) not only decreases the primary tumor growth rate but also significantly reduces relative liver weight and the amount of liver metastasis, compared to the control group. |
| In vivo | PP2, at concentrations of 1-100 mM, dose-dependently inhibits the growth of the human colon (SW480, HT29, and PMCO1), liver (KYN-2, Li7, PLC/PRF/5, and HepG2), and breast (MDA-MB-468, MCF-7, and BT-474) cancer cells. At 5 µM concentration, PP2 suppresses the phosphorylation and signaling of RET/PTC1 oncoprotein in lysis of NIH3T3 and NIH-RET/PTC3 cells. Additionally, 5 µM PP2 inhibits serum-independent growth in transformed NIH3T3 fibroblasts, and human papillary thyroid carcinoma cell lines TPC1 and FB2 with spontaneous RET/PTC1 rearrangements, as well as hampers Type I collagen matrix invasion by TPC1 cells. At 10 µM, PP2 downregulates the expression levels of pSrc-Y416, pEGFR-Y845, and pEGFR-Y1173 in HeLa and SiHa cells, and regulates cell cycle arrest by upregulating p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1), and downregulating cyclin A, cyclin-dependent kinases-2 and -4 (Cdk-2, -4) in HeLa cells, and cyclin B and Cdk-2 in SiHa cells. A 20 μM concentration of PP2 inhibits 40-50% of HT29 cell growth within an hour, reduces Src activity maintaining 35% inhibition for two days, and significantly promotes aggregation in most cancer cell lines (HT29, SW480, PMCO1, PLC/PRF/5, KYN-2, Li7, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-468) in an E-cadherin-dependent manner. In cancer cells, 20 μM PP2 boosts E-cadherin expression and its association with the actin cytoskeleton, as well as enhances α-catenin, β-catenin, and γ-catenin expression in HT29 cells, while in PLC/PRF/5 and MCF-7 cells, α-catenin protein levels remain unchanged, and β-catenin and γ-catenin levels slightly increase. |
| Kinase Assay | Immune complex enzyme assays: The acid-treated enolase is diluted 1:20 with 1× PBS before aliquoting 100 mL/well into a Nunc 96-well high protein binding assay plate. Assay wells are then aspirated; blocked with 0.5% bovine serum, 1× PBS for 1 h at 37 ℃;and then washed five times with 300 mL of 1× PBS/well. The source of Lck is either LSTRA cells or Lck expressed in HeLa cells using a vaccinia expression system. FynT is expressed in HeLa cells using the vaccinia system. Cells (12.5× 106/mL) are lysed in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, and 23 trypsin inhibitory units/mL aprotinin), and the lysates are clarified by centrifugation at 14,000 cpm for 15 min at 4 ℃ in an Eppendorf tube. The clarified lysates are then incubated with the appropriate anti-kinase antibody at 10 μg/mL for 2 h at 4 ℃. Protein A-Sepharose beads are added to the antibody/lysate mixture at 250 μL/mL and allowed to incubate for 30 min at 4 ℃. The beads are then washed twice in 1 mL of lysis buffer and twice in 1 mL of kinase buffer (25 mM HEPES, 3 mM MnCl2, 5 mM MgCl2, and 100 μM sodium orthovanadate) and resuspended to 50% (w/v) in kinase buffer. Twenty-five microliters of the bead suspension is added to each well of the enolase-coated 96-well high protein binding plate together with an appropriate concentration of compound and [γ-32P]ATP (25 μL/well of a 200 μCi/mL solution in kinase buffer). After incubation for 20 min at 20 ℃, 60 μLl of boiling 2× solubilization buffer containing 10 mM ATP is added to the assay wells to terminate the reactions. Thirty microliters of the samples is removed from the wells, boiled for 5 min, and run on a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gels are subsequently dried and exposed to Kodak X-AR film. For quantitation, films are scanned using a Molecular Dynamics laser scanner, and the optical density of the major substrate band, enolase p46, is determined.In companion experiments for measuring the activity of compounds against Lck, the assay plate is washed with two wash cycles on a Skatron harvester using 50 mM EDTA, 1 mM ATP. Scintillation fluid (100 μL) is then added to the wells, and 32P incorporation is measured using a micro-β-counter. |
| Cell Research | Cell viability is determined using an in vitro toxicology assay kit following the manufacturer's instructions. Cells are seeded in 96-well plates at day 0. Starting at day 1, cells are treated for 2 days with each of a series of increasing concentrations of PP2 (1 μM, 10 μM, and 100 μM). At the end of this period, cell proliferation is evaluated by a colorimetric assay based on the cleavage of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide by mitochondria dehydrogenase in viable cells, leading to formazan formation. This experiment is repeated three times with 10 determinations/tested concentration.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | AGL 1879, AG 1879 |
| Molecular Weight | 301.77 |
| Formula | C15H16ClN5 |
| Cas No. | 172889-27-9 |
| Smiles | NC1=C2C(=NN(C(C)(C)C)C2=NC=N1)C3=CC=C(Cl)C=C3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.35 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 56 mg/mL (185.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (6.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.