Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

SD-169 (SD 169) is a selective and ATP competitive the MAP kinases p38α and p38β inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $73 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $107 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | SD-169 (SD 169) is a selective and ATP competitive the MAP kinases p38α and p38β inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | p38α MAPK:3.2 nM (IC50), p38β MAPK:122 nM (IC50) |
| In vivo | Animals were gavaged with Scios SD-169 (10 or 30 mg/kg) or excipient (PEG300) 1 day before and daily after crush injury to the sciatic nerve.?SD-169 is a proprietary oral inhibitor of p38 MAPK activity.?The rate of axonal regeneration was determined by the functional pinch test and was significantly increased in treated animals 8 days after crush injury (P < 0.05;?30 mg/kg dose).?In SD-169-treated animals with nerve transection, nerve fibers regenerating through a silicone chamber were morphologically more mature than untreated nerves when observed 28 days after transection.?TNF immunofluorescence of distal nerve segments after crush injury suggested that SD-169 reduced SC TNF protein[1]. |
| Alias | SD 169 |
| Molecular Weight | 160.17 |
| Formula | C9H8N2O |
| Cas No. | 1670-87-7 |
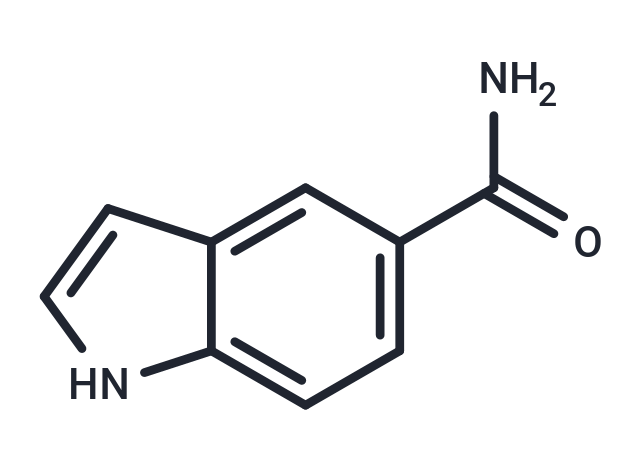
| Smiles | NC(=O)c1ccc2[nH]ccc2c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.328g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 10 mg/mL (62.43 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.