Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Adezmapimod (SB 203580) is a selective, ATP-competitive p38 MAPK inhibitor (IC50=0.3-0.5 μM) that activates autophagy and mitochondrial autophagy, with more than 100-fold higher selectivity over PKB, LCK, and GSK-3β.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $100 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $173 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $292 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Adezmapimod (SB 203580) is a selective, ATP-competitive p38 MAPK inhibitor (IC50=0.3-0.5 μM) that activates autophagy and mitochondrial autophagy, with more than 100-fold higher selectivity over PKB, LCK, and GSK-3β. |
| Targets&IC50 | p38 MAPK:0.3-0.5 μM (THP-1 cells), PKB:3-5 μM (THP-1 cells) |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2 were treated with Adezmapimod (0.1-20 μM) for 30 min, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Adezmapimod dose-dependently activated ERK but not p38 and JNK, and the maximum activation of ERK was between 1-10 μM. [1] METHODS: CD4+ T cells were treated with Adezmapimod (1-25 μM) for 72 h. The proliferation of Tregs was analyzed by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Adezmapimod inhibited TNF-induced proliferation of Tregs in a dose-dependent manner, with inhibition rates ranging from 32.0-73.2%. Adezmapimod treatment also significantly reduced the proportion of Foxp3+ Tregs in cultured CD4+ T cells, with inhibition rates ranging from 24.9-47.05%. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To examine the in vivo activity, Adezmapimod (25 mg/kg in 4% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+61% ddH2O) was administered to LPS-treated C57BL/6J mice by a single intraperitoneal injection, and then the mice were killed 24 and 72 h later. RESULTS: The LPS-induced up-regulation of Ki-67 and TNFR2 expression on Tregs was completely eliminated by Adezmapimod treatment. The inhibitory effect of Adezmapimod on the proliferation of Tregs in LPS-treated mice lasted for at least 72 h. [2] METHODS: To detect the effects on endometriosis (EM) development, Adezmapimod (1 μg/mg) was injected intraperitoneally into EM-induced BALB/c mice once daily for twenty-four days. RESULTS: Adezmapimod reduced the weight and size of endometriotic lesions in mice. Levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-2, and MMP-9 were reduced in peritoneal cells in the Adezmapimod group compared to the EM group. p38 MAPK phosphorylation levels were elevated in the EM group, and Adezmapimod down-regulated phosphorylation levels. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | Cells were lysed in Buffer A for Western blotting and PKB kinase assays. Kinase assays were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, 4 μg of sheep anti-PKBα was immobilized on 25 μl of protein G-Sepharose overnight (or 1.5 h) and washed in Buffer A (50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mMEGTA, 0.5 mM Na3VO4, 0.1% β-mercaptoethanol, 1% Triton X-100, 50 mM sodium fluoride, 5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 μg/ml aprotinin, pepstatin, leupeptin, and 1 μM microcystin). The immobilized anti-PKB was then incubated with 0.5 ml of lysate (from 5 × 10^6 cells) for 1.5 h and washed three times in 0.5 ml of Buffer A supplemented with 0.5 M NaCl, two times in 0.5 ml of Buffer B (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.03% (w/v) Brij-35, 0.1 mM EGTA, and 0.1% β-mercaptoethanol), and twice with 100 μl of assay dilution buffer; 5× assay dilution buffer is 100 mM MOPS, pH 7.2, 125 mMβ-glycerophosphate, 25 mM EGTA, 5 mM sodium orthovanadate, 5 mM DTT. To the PKB enzyme immune complex was added 10 μl of assay dilution buffer, 40 μM protein kinase A inhibitor peptide, 100 μM PKB-specific substrate peptide, and 10 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, all made up in assay dilution buffer. The reaction was incubated for 20 min at room temperature with shaking, then samples were pulse spun, and 40 μl of reaction volume were removed into another tube to which was added 20 μl of 40% trichloroacetic acid to stop the reaction. This was mixed and incubated for 5 min at room temperature, and 40 μl was transferred onto P81 phosphocellulose paper and allowed to bind for 30 s. The P81 pieces were washed three times in 0.75% phosphoric acid then in acetone at room temperature. γ-32P incorporation was then measured by scintillation counting [1]. |
| Cell Research | The luciferase reporter plasmid pIL6luc(-122) and the CAT reporter plasmid p(TRE)5CAT were transfected into TF-1 cell line by means of electroporation. Prior to transfection, cells were cultured for 16?h at a density of 0.5×10^6 cells/ml in the appropriate medium, washed twice and resuspended in RPMI 1640 at a density of 10×10^6 in 200?μl. When transfected with a single plasmid, 25?μg of DNA was added and the mixture was left at room temperature for 15?min. Cotransfections were performed with 15?μg of the reporter plasmid pIL6luc(-122) together with 15?μg of the dominant-negative expression plasmids (pRSV-MKK3(Ala), pcDNA3-MKK6(K82A), pRSV-NΔRaf1, pcDNA3-MKK4(Ala), pcDNA3-Flag-JNK1, or pcDNA3 (empty vector). Cotransfections of pGAL4tkluc (5?μg) with either pGAL4p65 (5?μg) or pGAL4dbd (5?μg) were performed under similar conditions. In addition, cells were cotransfected with 2?μg of a CMV-CAT plasmid, to normalize for transfection efficiency. Electroporation, in 0.4?cm electroporation cuvettes, was performed at 240?V and 960?μF with Gene Pulser electroporator. After electroporation, the cells were replated in RPMI 1640 containing 2% FBS. Six hours after transfection cells were stimulated for 24?h with medium or OA (30?ng/ml) or SB203580 for 30?min prior to OA stimulation. The cells were then harvested and lysed by commercially available luciferase lysis buffer. One-hundred μl of lysis product was added to 100?μl of luciferase assay reagents and luciferase activity was measured with the Anthos Lucy1 luminometer. CAT reporter activity of 100?μl lysis product plus 100?μl CAT dilution buffer was determined with a commercially available CAT Elisa kit [3]. |
| Animal Research | In survival studies, C57BL/6J mice weighing 20 g to 30 g were briefly anesthetized with isoflurane and challenged with 0.05 mL of IT normal saline (NS, noninfected controls) or E. coli (15 × 10^9 CFU/kg) as previously described. One hour before NS challenge, mice (n = 24) received either intraperitoneal SB203580 (100 mg/kg in 0.25 mL) or diluent only (placebo). Infected animals received SB203580 in doses of 100, 10, 1, or 0.1 mg/kg or placebo 1 hour before IT E. coli (n = 241); SB203580 100 or 0.1 mg/kg or placebo 1 hour after E. coli (n = 121); or SB203580 100 mg/kg or placebo 12 hours after E. coli (n = 72). All animals received ceftriaxone (100 mg/kg in 0.1 mL, subcutaneously) for 4 days and NS (0.5 mL, subcutaneously) for 1 day beginning 4 hours after challenge. Animals were observed every 2 hours for the initial 48 hours, every 4 hours from 48 hours to 72 hours, every 8 hours from 72 hours to 96 hours, and then twice daily until study completion (168 hours). Sequential weekly experiments with 24 animals each compared either two to three doses of SB203580 versus placebo administered at similar times or similar doses of SB203580 versus placebo at differing treatment times. Study groups in each experiment were of equivalent sample size (i.e., 6 – 8 per group) [5]. |
| Alias | SB203580, RWJ 64809, PB 203580 |
| Molecular Weight | 377.43 |
| Formula | C21H16FN3OS |
| Cas No. | 152121-47-6 |
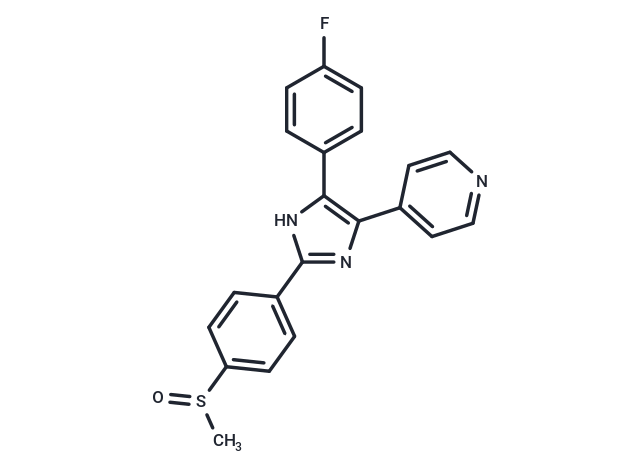
| Smiles | FC1=CC=C(C2=C(N=C(N2)C3=CC=C(S(C)=O)C=C3)C=4C=CN=CC4)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.42 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (13.25 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (132.47 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.