Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Urea (Carbonyldiamide) is formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end metabolite of protein catabolism and accounts for about one-half of the total urinary solids.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $46 | In Stock |
| Description | Urea (Carbonyldiamide) is formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end metabolite of protein catabolism and accounts for about one-half of the total urinary solids. |
| Alias | Ureophil, E-Cardamoni, Carbonyldiamide, Carbamide |
| Molecular Weight | 60.06 |
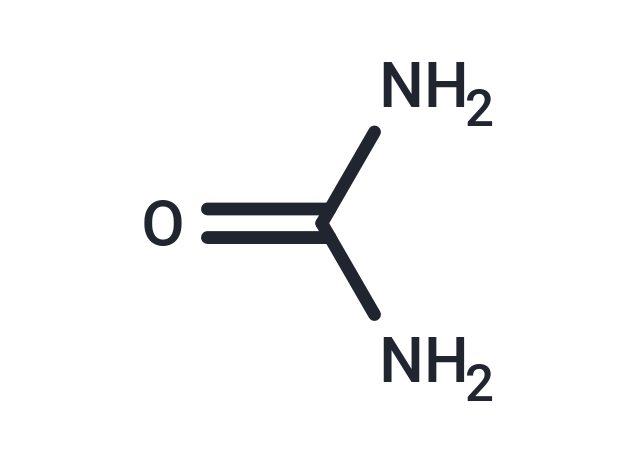
| Formula | CH4N2O |
| Cas No. | 57-13-6 |
| Smiles | C(N)(N)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.33 g/cm3. Temperature:20 °C. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (999 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 199.8 mM, Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.