Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

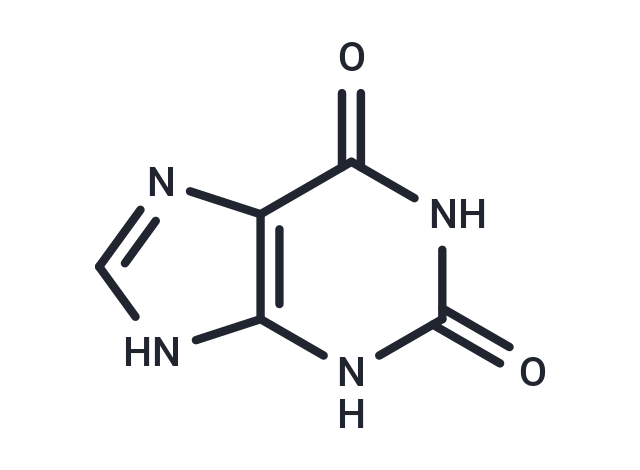
Xanthine (Isoxanthine) is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the Xanthine oxidase enzyme. Xanthine is found in most body tissues and fluids in various organisms. Biologically Xanthine is produced from guanine by cypin (guanine deaminase). Furthermore, Xanthines act as antagonists for adenosine receptors, with selectivity depending on whether there are substitution of alkyl groups.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Xanthine (Isoxanthine) is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the Xanthine oxidase enzyme. Xanthine is found in most body tissues and fluids in various organisms. Biologically Xanthine is produced from guanine by cypin (guanine deaminase). Furthermore, Xanthines act as antagonists for adenosine receptors, with selectivity depending on whether there are substitution of alkyl groups. |
| Alias | Isoxanthine, 2,6-Dihydroxypurine |
| Molecular Weight | 152.11 |
| Formula | C5H4N4O2 |
| Cas No. | 69-89-6 |
| Smiles | O=C1NC2=C(N=CN2)C(=O)N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.5452 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.52 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.