Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Adrenalone hydrochloride (Adrenalone HCl) is a dopamine β-oxidase inhibitor with a similar structure to the norepinephrine transporter (NET) ligand, with an IC50 of 36.9 μM. It is an adrenergic agonist that acts as a local vasoconstrictor and hemostatic agent.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $43 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $148 | In Stock |
| Description | Adrenalone hydrochloride (Adrenalone HCl) is a dopamine β-oxidase inhibitor with a similar structure to the norepinephrine transporter (NET) ligand, with an IC50 of 36.9 μM. It is an adrenergic agonist that acts as a local vasoconstrictor and hemostatic agent. |
| In vitro | Adrenalone is the ketone form of adrenaline, which is used as a topical hemostatic agent, vasoconstrictor, and nasal vasoconstrictor. In a nitrogenated aqueous solution containing 10 or 100 mM tert-butanol, Adrenalone (0.1 mM) reduces Adrenalone by hydration of electrons, resulting in the same transient spectrum, and thus all OH radicals are scavenged. Although Adrenalone acted similarly to carbonyl compounds in the reduction process, it was mainly controlled by catechol functional groups in the oxidation reaction. Adrenalone (12 μM) inhibited the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine by inhibiting dopamine β-oxidase. Unlike Epinine, which has a keto group in the β-site, Adrenalone contains an amine group (ionic bond with Asp75), an aromatic ring (hydrophobic interactions with Tyr152, Phe72, and Phe317), and a hydroxyl group (hydrogen bonding with Ala145).10 μM and 100 μM Adrenalone 10 μM and 100 μM Adrenalone reduced substrate uptake by 99% and 27%, respectively. |
| In vivo | Adrenalone is the ketone form of adrenaline, which is used as a topical hemostatic agent, vasoconstrictor, and nasal vasoconstrictor. In a nitrogenated aqueous solution containing 10 or 100 mM tert-butanol, Adrenalone (0.1 mM) reduces Adrenalone by hydration of electrons, resulting in the same transient spectrum, and thus all OH radicals are scavenged. Although Adrenalone acted similarly to carbonyl compounds in the reduction process, it was mainly controlled by catechol functional groups in the oxidation reaction. Adrenalone (12 μM) inhibited the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine by inhibiting dopamine β-oxidase. Unlike Epinine, which has a keto group in the β-site, Adrenalone contains an amine group (ionic bond with Asp75), an aromatic ring (hydrophobic interactions with Tyr152, Phe72, and Phe317), and a hydroxyl group (hydrogen bonding with Ala145).10 μM and 100 μM Adrenalone 10 μM and 100 μM Adrenalone reduced substrate uptake by 99% and 27%, respectively. |
| Alias | Adrenalone HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 217.65 |
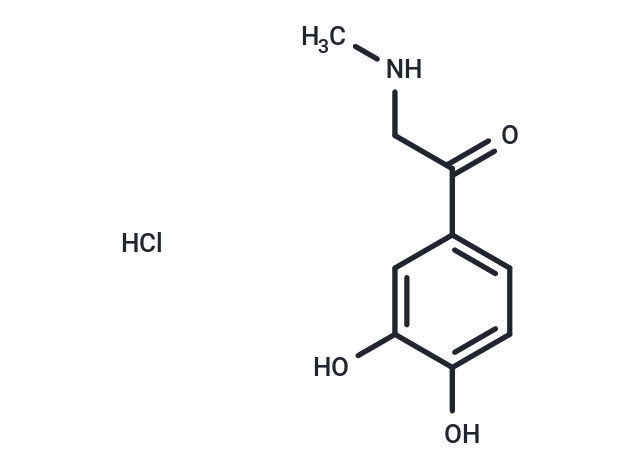
| Formula | C9H11NO3·HCl |
| Cas No. | 62-13-5 |
| Smiles | Cl.CNCC(=O)c1ccc(O)c(O)c1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 60 mg/mL (275.67 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 40 mg/mL (183.78 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.