Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

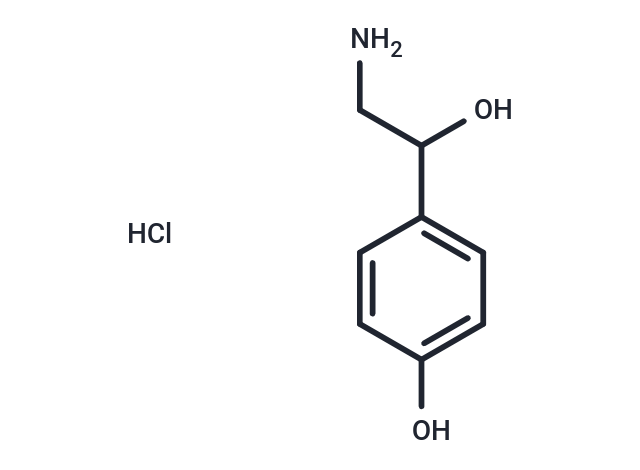
Octopamine hydrochloride ((±)-p-Octopamine hydrochlorid) is a biogenic monoamine structurally associated with noradrenaline. It can serve as a neurohormone, a neurotransmitter, and a neuromodulator in invertebrates.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $45 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $53 | In Stock |
| Description | Octopamine hydrochloride ((±)-p-Octopamine hydrochlorid) is a biogenic monoamine structurally associated with noradrenaline. It can serve as a neurohormone, a neurotransmitter, and a neuromodulator in invertebrates. |
| In vitro | Octopamine is present in relatively high concentrations in neuronal as well as in non-neuronal tissues of most invertebrate species studied, and modulates almost every physiological process. Octopamine acts as neurohormone including desensitization of sensory inputs, influence on learning and memory, or regulation of the mood of the animal in the central nervous system. Octopamine is the only neuroactive non-peptide transmitter whose physiological role is restricted to invertebrates, and all octopamine receptors belong to the family of G-protein coupled receptors. [1] |
| In vivo | Octopamine (10 mg/mL) is necessary for the acquisition of sugar memory in Drosophila. [2] Octopamine treatment increases responsiveness to brood pheromone and decreased responsiveness to social inhibition. Octopamine acts as an important source of variation in response thresholds and as a modulator of pheromonal communication in insect societies. [3] Octopamine (10 μM) injected into the mushroom body (MB) calyces or the antennal lobe but not the lateral protocerebral lobe produces a lasting, pairing-specific enhancement of extension of the proboscis. Octopamine (10 μM) injected into the MB calyces results in an additional pairing-specific effect, because it does not lead to an acquisition but a consolidation after conditioning. [4] Octopamine treatment significantly elevates levels of octopamine in the brain and caused a significant dose-dependent increase in the number of new foragers. Octopamine treatment is effective only when given to bees old enough to forage, i.e., older than 4 days of age. Octopamine influences division of labor in honey bee colonies. [5] |
| Alias | (±)-p-Octopamine hydrochlorid, (+,-)-Octopamine HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 189.639 |
| Formula | C8H12ClNO2 |
| Cas No. | 770-05-8 |
| Smiles | Cl.NCC(O)c1ccc(O)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.39 g/cm3 at 20℃ |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (87.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 200.4 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.