Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid is a derivative of aspartic acid, synthesized in neurons from the amino acid aspartic acid and acetyl coenzyme A. N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid has antioxidant activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $163 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $247 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $418 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $595 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $162 | In Stock |
| Description | N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid is a derivative of aspartic acid, synthesized in neurons from the amino acid aspartic acid and acetyl coenzyme A. N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid has antioxidant activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | DPPH free radical scavenging:19.49 μM (IC50), AChE:57.50-2.43 μg/mL (IC50), CYP2D6:0.761 μM (IC50) |
| In vitro | Quantification of these compounds was performed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). To investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of the compounds, DPPH radical scavenging, NBT superoxide scavenging and nitric oxide production inhibitory activities were examined in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells. We suggest that the major active components of RRS are herbacetin glycosides, exhibiting antioxidant activity, and kaempferol, exhibiting anti-inflammatory activity.In this study, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity and nitrotetrazolium blue chloride (NBT) superoxide scavenging activity were measured to assess the antioxidant activity of the components from RRS. DPPH has the ability to easily accept hydrogen atoms because it contains an unstable element, the hydrazyl nitrogen, therefore, antioxidant activity can be measured because DPPH loses its violet color when it receives hydrogens from antioxidants. Additionally, NBT has the ability to easily receive superoxide because it contains unstable anions. Therefore, antioxidant activity may be measured when NBT loses its yellow color upon reaction with abundant superoxide. Among the compounds from RRS, 7(Rhodionin) and 8 exhibited the most potent DPPH free radical scavenging activities, with IC50 values of 19.49 ± 0.21 and 27.77 ± 0.61 μM, respectively, compared to the positive control, L-ascorbic acid (IC50 = 32.89 ± 0.70 μM). The other compounds did not exhibit activities in this assay up to 100 μM (Table 2). |
| Molecular Weight | 448.38 |
| Formula | C21H20O11 |
| Cas No. | 85571-15-9 |
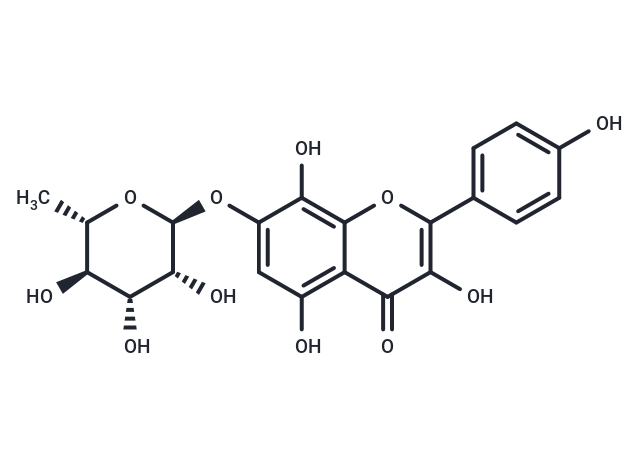
| Smiles | C[C@@H]1O[C@@H](Oc2cc(O)c3c(oc(-c4ccc(O)cc4)c(O)c3=O)c2O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.737 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (111.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.