Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

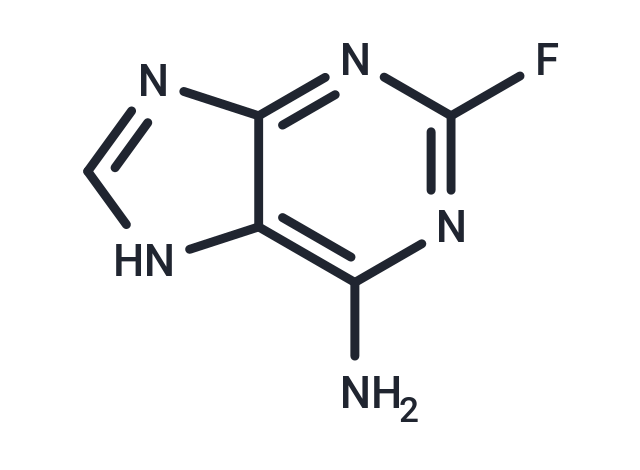
2-Fluoroadenine (NSC-27364) has toxicity in nonproliferating and proliferating tumor cells. 2-Fluoroadenine can be used for anticancer studies.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $29 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
| Description | 2-Fluoroadenine (NSC-27364) has toxicity in nonproliferating and proliferating tumor cells. 2-Fluoroadenine can be used for anticancer studies. |
| In vitro | In Balb-3T3 cells, 2-Fluoroadenine (0.22, 2.2 and 22 μM; 30 hours) inhibits protein, RNA, and DNA syntheses. In CEM cells, 2-Fluoroadenine (2 μM; 4 hours) inhibits CEM cell growth by targeting one or more enzymes involved in either RNA or protein synthesis. In nonproliferating MRC-5 cells, 2-Fluoroadenine (0-1000 μM; 96 hours) exhibits cytotoxicity[2]. |
| Alias | NSC-27364, NSC27364, NSC 27364 |
| Molecular Weight | 153.12 |
| Formula | C5H4FN5 |
| Cas No. | 700-49-2 |
| Smiles | NC1=C2NC=NC2=NC(F)=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.739 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 4.4 mg/mL (26.97 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.