Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

ABT-702 dihydrochloride is a highly potent inhibitor of adenosine kinase (AK).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $79 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $122 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $197 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $558 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $788 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,660 | 2-4 weeks | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $143 | In Stock |
| Description | ABT-702 dihydrochloride is a highly potent inhibitor of adenosine kinase (AK). |
| Targets&IC50 | Adenosine kinase:1.7nM |
| In vitro | ABT-702 is an orally effective adenosine kinase inhibitor with a high selectivity over other adenosine (ADO) interaction sites (A1, A2A, A3 receptors, ADO transporter, and ADO deaminase). It demonstrates equipotency (IC50=1.5±0.3 nM) in inhibiting human native AK (placenta), two human recombinant isoforms (AKlong and AKshort), and AK from monkey, dog, rat, and mouse brain. ABT-702 also strongly inhibits AK activity in intact cultured IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells (IC50=51 nM), indicating its ability to penetrate the cell membrane and inhibit intracellular AK effectively. |
| In vivo | Rats received an intraperitoneal injection of DPCPX (3 mg/kg), ABT-702 (3 mg/kg), or a control substance 10 minutes before an intravenous dose of 2-18F-fluorodeoxy-D-glucose (FDG) (15.4±0.7 MBq per rat), followed by a 15-minute static PET scan. Images were standardized against an FDG PET template for rats, with standard uptake values (SUVs) calculated. Despite no change in overall brain FDG uptake due to drug treatment, significant regional reductions in metabolism, especially in the cerebellum, were observed in rats treated with DPCPX and ABT-702 compared to those receiving the control substance, indicating a modest effect of endogenous adenosine on FDG accumulation in a non-stimulated state. Body weight and blood glucose levels were consistent across all groups. Vehicle, ABT-702, and DPCPX treatment resulted in similar whole-brain PET SUVs (1.6±0.4, 1.6±0.6, and 1.8±0.6, respectively; F(2,9)=0.298, P=0.75), with statistical parametric mapping analysis identifying significant hypometabolism in the cerebellum and mesencephalon. ABT-702 markedly reduced acute thermal nociception in mice in a dose-dependent manner following both intraperitoneal (ED50=8 μmol/kg) and oral (ED50=65 μmol/kg) administration, as evidenced in the hot-plate test. This antinociceptive effect was further supported by dose-dependent results in the abdominal constriction assay (ED50=2 μmol/kg i.p.). |
| Animal Research | Rats are fasted for 16 hours prior to use. At the beginning of the experiment, each rat is weighed, and then anesthetized using 5% isoflurane for induction and 2.5% for maintenance. A blood sample from tail vein is collected for a fasting blood glucose determination using a standard glucometer. Rats are then given an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of DPCPX (3 mg/kg, n=4), ABT-702 (3 mg/kg, n=4), or an equivalent volume of vehicle (15% dimethyl sulfoxide, 15% cremophor EL, 70% saline, n=4) to manipulate the effect of endogenous adenosine on neuronal activities. Ten minutes after i.p. injection, rats are administered FDG (15.4±0.7 MBq) in 0.3-0.5 mL saline by intravenous (i.v.) tail vein injection. Rats are allowed to recover from anesthesia after the FDG injection but are reanesthetized for 15-minute-static PET scan with the head in the center of the field of view. |
| Molecular Weight | 536.25 |
| Formula | C22H21BrCl2N6O |
| Cas No. | 1188890-28-9 |
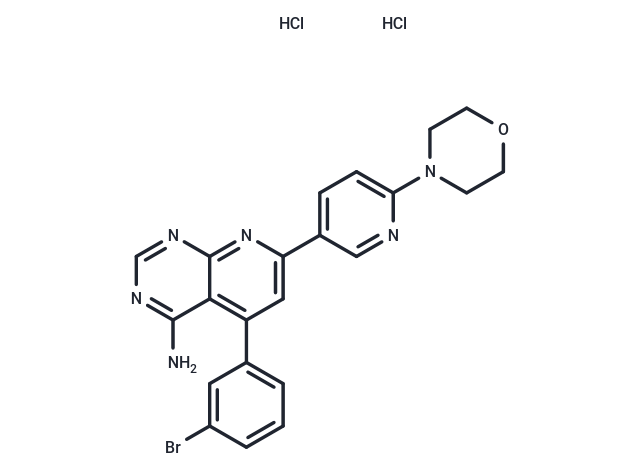
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.Nc1ncnc2nc(cc(-c3cccc(Br)c3)c12)-c1ccc(nc1)N1CCOCC1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (83.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.