Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Alexidine dihydrochloride has antifungal and antibiofilm activity against a diverse range of fungal pathogens. Alexidine dihydrochloride is an anticancer agent that targets a mitochondrial tyrosine phosphatase, PTPMT1, in mammalian cells and causes mitochondrial apoptosis. Thus, Alexidine dihydrochloride has the potential to be developed as a pan-antifungal, antibiofilm drug.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $54 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $101 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $32 | In Stock |
| Description | Alexidine dihydrochloride has antifungal and antibiofilm activity against a diverse range of fungal pathogens. Alexidine dihydrochloride is an anticancer agent that targets a mitochondrial tyrosine phosphatase, PTPMT1, in mammalian cells and causes mitochondrial apoptosis. Thus, Alexidine dihydrochloride has the potential to be developed as a pan-antifungal, antibiofilm drug. |
| In vitro | Alexidine dihydrochloride effectively eliminates mature biofilms of Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus spp., which are typically resistant to nearly all antifungal drugs, at low concentrations (1.5 to 6 μg/mL). It exhibits potent activity against most strains of Candida, achieving minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of ≤1.5 μg/mL for all tested isolates in planktonic form, except for Candida parapsilosis and Candida krusei. Notably, it also demonstrates significant effectiveness against fluconazole-resistant Candida isolates, including strains of C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. parapsilosis, and C. auris. Furthermore, Alexidine dihydrochloride prevents the growth and spread of fungi by entirely inhibiting filamentation and biofilm dispersal, specifically at concentrations significantly lower than those harmful to human cells (150 ng/mL versus 5- to 10-fold higher concentrations for 50% killing of HUVECs and lung epithelial cells). |
| In vivo | The study primarily investigates biofilm formation by C. Albicans, leveraging an established murine biofilm model for evaluating both existing and novel antifungal compounds. Alexidine dihydrochloride is highlighted for its efficacy, inhibiting 67% of fungal biofilm growth and viability in comparison to control groups, as evidenced by fungal colony-forming unit (CFU) counts. Additionally, microscopic examination of 24-hour-old biofilms within mice jugular vein catheters demonstrates a considerably reduced biofilm density when treated with Alexidine dihydrochloride[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 581.71 |
| Formula | C26H58Cl2N10 |
| Cas No. | 1715-30-6 |
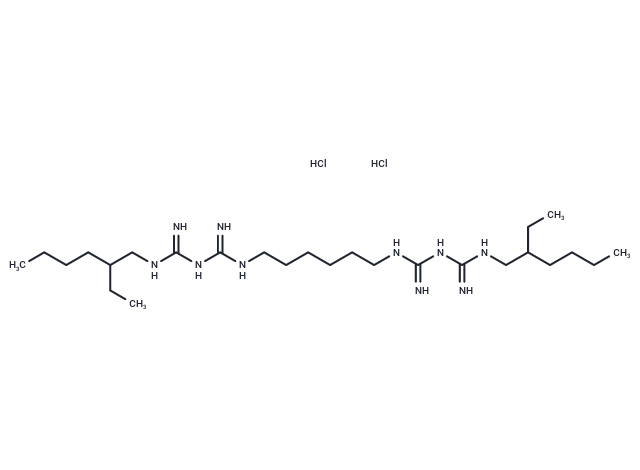
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.CCCCC(CC)CNC(=N)NC(=N)NCCCCCCNC(=N)NC(=N)NCC(CC)CCCC |
| Relative Density. | 1.1g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (429.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.