Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

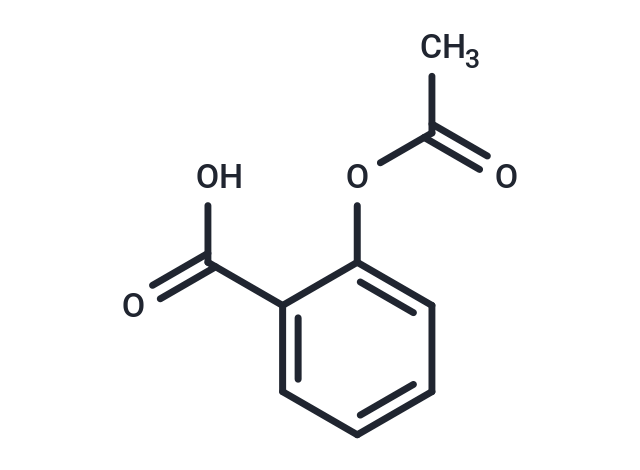
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid) is a COX inhibitor that inhibits COX1 and COX2 (IC50=5/210 μg/mL) with selective, irreversible, and oral activity. Aspirin is also a histone deacetylase inhibitor that up-regulates the cell cycle blocking protein, p21. Aspirin has a variety of activities. Aspirin has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic, and antiplatelet aggregation activities.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $53 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $87 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid) is a COX inhibitor that inhibits COX1 and COX2 (IC50=5/210 μg/mL) with selective, irreversible, and oral activity. Aspirin is also a histone deacetylase inhibitor that up-regulates the cell cycle blocking protein, p21. Aspirin has a variety of activities. Aspirin has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic, and antiplatelet aggregation activities. |
| Targets&IC50 | COX-1:5μg/mL, COX-2:210 μg/mL |
| In vitro | METHODS: Colorectal cancer cells SW620, LoVo, RKO and DLD-1 were treated with Aspirin (2 mM) and Cisplatin (5-80 µM) for 48 h. Cell viability was detected by MTT assay. RESULTS: The combination more effectively reduced the viability of colon cancer cells. The combination treatment resulted in a significant decrease in the IC50 value of Cisplatin. [1] METHODS: Osteoblasts MG-63 were treated with Aspirin (1-1000 µM) for 24 h. Cell cycle was detected by Flow cytometry. RESULTS: Aspirin at doses of 1, 10, and 20 µM had no significant effect on the MG-63 cell cycle after 24 h of treatment. However, the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase was significantly increased at doses of 100 and 1000 µM. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay in vivo antitumor activity, Aspirin (100 mg/kg administered by gavage once daily) and Cisplatin (3 mg/kg administered intraperitoneally every three days) were administered to nude mice bearing LoVo xenografts for 18 days. RESULTS: Aspirin and Cisplatin synergistically inhibited the growth of colon cancer grafts in nude mice, and these effects were exerted, at least in part, through modulation of the PI3K-Akt, RAF-MEK-ERK, and NF-κB/COX-2 signaling pathways. [1] |
| Cell Research | Chondrocytes are isolated from articular cartilage of donors with no articular disease. Unstimulated and interleukin 1 (IL-1) stimulated chondrocytes are used as models to study the effects of drugs on COX-1 and COX-2. Cells are incubated with vehicle or drugs (Asprin); supernatants are removed and the level of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in each sample is determined by enzyme immunoassay. IC50s are calculated from the reduction in PGE2 content by different concentrations of the test substance by linear regression analysis[5]. |
| Alias | ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid, Acetylsalicylate |
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
| Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Cas No. | 50-78-2 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 1.8 mg/mL (9.99 mM), Please add co-solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. H2O: 1.80 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (277.53 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10% DMSO+90% Saline/H2O/DMSO
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.