Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

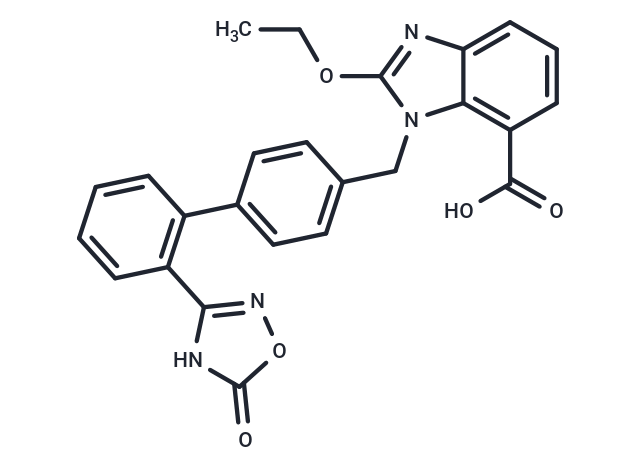
Azilsartan (TAK-536) is an Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blocker that acts as an Angiotensin 2 Type 1 Receptor Antagonist, leading to a physiologic effect of decreased blood pressure.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $80 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $118 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $33 | In Stock |
| Description | Azilsartan (TAK-536) is an Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blocker that acts as an Angiotensin 2 Type 1 Receptor Antagonist, leading to a physiologic effect of decreased blood pressure. |
| Targets&IC50 | AT1 receptor:2.6 nM |
| In vitro | Azilsartan inhibits the specific binding of 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII to human angiotensin type 1 receptors. Azilsartan also inhibits the accumulation of AII-induced inositol 1-phosphate (IP1) in the cell-based assay with an IC50 value of 9.2 nM. In isolated rabbit aortic strips, Azilsartan reduces the maximal contractile response to AII with a pD'2 value of 9.9. The inhibitory effects of Azilsartan on contractile responses induced by AII persists after the strips are washed. [1] Azilsartan suppresses the increase in plasma glucose level in the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) without significant change in insulin concentration and improved insulin sensitivity. In skeletal muscle, Azilsartan decreases the expression of TNF-α at doses of 0.001%. In adipose tissue, Azilsartan reduces TNF-α expression but increases the expression of adiponectin, PPARγ, C/EBα, and aP2. [2] In cultured 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, Azilsartan enhances adipogenesis and exertes greater effects than valsartan on expression of genes encoding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα), PPARδ, leptin, adipsin, and adiponectin. Azilsartan also potently inhibits vascular cell proliferation in the absence of exogenously supplemented angiotensin II. [3] |
| In vivo | In Koletsky rats, Azilsartan treatment lowers blood pressure, basal plasma insulin concentration and the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index, and inhibited over-increase of plasma glucose and insulin concentrations during oral glucose tolerance test. Azilsartan downregulates 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 expression. [4] |
| Kinase Assay | Radioligand binding studies on human AT1 receptors: A radioligand binding assay is performed by using human AT1 receptor-coated microplates containing 4.4 to 6.2 fmol of receptors/well (10 μg of membrane protein/well). Membrane-coated wells are incubated with 45 μL of assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.005% CHAPS, pH 7.4) containing various concentrations of Azilsartan at room temperature. After 90 minutes, 5 μL of 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII (final concentration 0.6 nM) dissolved in assay buffer is added to the wells, and the plate is incubated for 5 hours. In each step, the plate is briefly and gently shaken on a plate shaker. In washout experiments, the membranes are incubated with Azilsartan for 90 minutes, then immediately washed twice with 200 μL/well of assay buffer to remove unbound compounds, and further incubated for 5 hours with 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII. Membrane-bound radioactivity is counted using a TopCount Microplate Scintillation and Luminescence Counter. In the experiments to estimate the dissociation rate of Azilsartan from AT1 receptors, membranes are incubated for 90 minutes with Azilsartan at a concentration of 30 nM for Azilsartan. Azilsartan inhibits the specific binding of 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII to human AT1 by approximately 90%. The membranes are then immediately washed twice with 200 μL/well of assay buffer and further incubated with 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII for 240 minutes. Membrane-bound radioactivity is counted using the TopCount Microplate Scintillation and Luminescence Counterat 30 minutes, 60 minutes, 90 minutes, 120 minutes, 150 minutes, 180 minutes, or 240 minutes. Nonspecific binding of 125I-Sar1-Ile8-AII is estimated in the presence of 10 μM unlabeled AII. Unlabeled AII is added again after washout for the washout experiment. Specific binding is defined as total binding minus nonspecific binding. |
| Cell Research | Twenty-four hours after transfections, the COS-7 cells expressing human AT1 receptors are starved by changing the culture medium to starvation buffer (1 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 4.2 mM KCl, 146 mM NaCl, 5.5 mM glucose, and 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.3). Then, 5 μL/well of Azilsartan dissolved in starvation buffer is added to the cells at the indicated concentrations, and they are pretreated for the indicated times. Two hours after starvation, LiCl is added to a final concentration of 50 mM with or without AII 10 nM, and the cells are further incubated for the indicated times at 37°C. In washout experiments, the cells are washed once with 100 μL/well of starvation buffer to remove unbound Azilsartan before stimulation with AII. The accumulation of inositol 1-phosphate (IP1) is measured by using an IP-One Tb kit. The fluorescence resonance energy transfer signal is measured on a plate reader.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | TAK-536 |
| Molecular Weight | 456.45 |
| Formula | C25H20N4O5 |
| Cas No. | 147403-03-0 |
| Smiles | C(N1C=2C(N=C1OCC)=CC=CC2C(O)=O)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=C(C=CC=C4)C5=NOC(=O)N5 |
| Relative Density. | 1.42 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 55 mg/mL (120.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.