Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

GDC-0152 is a potent inhibitor of IAPs.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $36 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $85 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $126 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $230 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $549 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $72 | In Stock |
| Description | GDC-0152 is a potent inhibitor of IAPs. |
| Targets&IC50 | CIAP1-BIR3:17 nM(Ki), MLXBIR3SG:14 nM(Ki), XIAP BIR3:28 nM(Ki), XIAP BIR2:112 nM(Ki), CIAP2-BIR3:43 nM(Ki) |
| In vitro | GDC-0152 inhibits protein−protein interactions between IAP proteins and pro-apoptotic molecules. It disrupts XIAP's binding to caspase-9 and the association of ML-IAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2 with Smac in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. Similarly, in melanoma SK-MEL28 cells, GDC-0152 abolishes the natural association between ML-IAP and Smac. It decreases cell viability in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line without affecting normal human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC). Furthermore, GDC-0152 activates caspases 3 and 7 dependent on dose and time, and induces rapid degradation of cIAP1 in A2058 melanoma cells at low concentrations, aligning with its affinity for cIAP1. |
| In vivo | GDC-0152 exhibits moderate hepatic clearance as inferred from metabolic stability assays using human liver microsomes, with its plasma-protein binding being moderate yet consistent across several species, including mice (88−91%), rats (89−91%), dogs (81−90%), monkeys (76−85%), and humans (75−83%) across investigated concentrations (0.1−100 μM); however, rabbits show higher plasma-protein binding rates (95−96%). Importantly, GDC-0152 does not show a preference for red blood cell distribution, as evidenced by blood-plasma partition ratios ranging from 0.6 to 1.1 across all tested species. Pharmacokinetic profiles reveal a maximum concentration (C max) of 53.7 μM and an area under the curve (AUC) of 203.5 h·μM. [1] |
| Kinase Assay | Fluorescence polarization-based competition assay: Inhibition constants ( Ki ) for the antagonists are determined by addition of the IAP protein constructs to wells containing serial dilutions of the antagonists or the peptide AVPW, and the Hid-FAM probe or AVP-diPhe-FAM probe, as appropriate, in the polarization buffer. Samples are read after a 30-minute incubation. Fluorescence polarization values are plotted as a function of the antagonist concentration, and the IC50 values are obtained by fitting the data to a 4-parameter equation using software. Ki values for the antagonists are determined from the IC50 valued. |
| Cell Research | MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cells and HMECs are treated with the indicated concentrations of GDC-0152. Cell death is assessed using the CellTiter-Glo luminescent cell viability assay 72 h following the start of treatment.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | GDC0152 |
| Molecular Weight | 498.64 |
| Formula | C25H34N6O3S |
| Cas No. | 873652-48-3 |
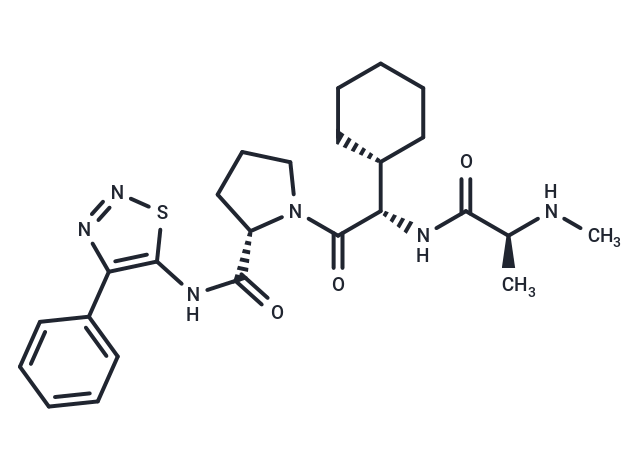
| Smiles | C([C@@H](NC([C@@H](NC)C)=O)[C@@H]1CCCCC1)(=O)N2[C@H](C(NC3=C(N=NS3)C4=CC=CC=C4)=O)CCC2 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 92 mg/mL (184.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 92 mg/mL (184.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 3 mg/mL (6.02 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO/Ethanol
DMSO/Ethanol
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.