Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sarcosine (Methylglycine) is a competitive inhibitor of the type I glycine transporter (GlyT1) and an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) co-agonist.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $55 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $133 | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $198 | In Stock |
| Description | Sarcosine (Methylglycine) is a competitive inhibitor of the type I glycine transporter (GlyT1) and an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) co-agonist. |
| In vitro | Sarcosine is a GlyR agonist in addition to being a GlyT1 inhibitor and NMDAR co-agonist, but it is less potent than glycine as a GlyR agonist and is not a full agonist[1]. The viability of the sarcosine-treated cells is significantly reduced[4]. |
| In vivo | Sarcosine has weak anticonvulsant properties[2]. It ameliorates (prepulse inhibition)PPI deficits in mGluR5 knockout mice[3]. |
| Cell Research | Immediately after the cells grow to 50-60% confluence, the cultivation medium is replaced by fresh medium to synchronise cell growth. Cells are cultivated for 24 h under these conditions. Subsequently, the culture medium is supplemented with sarcosine (N-methylglycine) diluted to a final concentration 10, 150, 250, 500, 1,000 and 1,500 μM. Treatment is carried out for 0, 6, 12, 24 and 72 h, and samples are collected at these strictly defined time points.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Sarcosinic acid, Sarcosin, N-methylglycine, N-Methylaminoacetic acid, Methylglycine, Methylaminoacetic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 89.09 |
| Formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Cas No. | 107-97-1 |
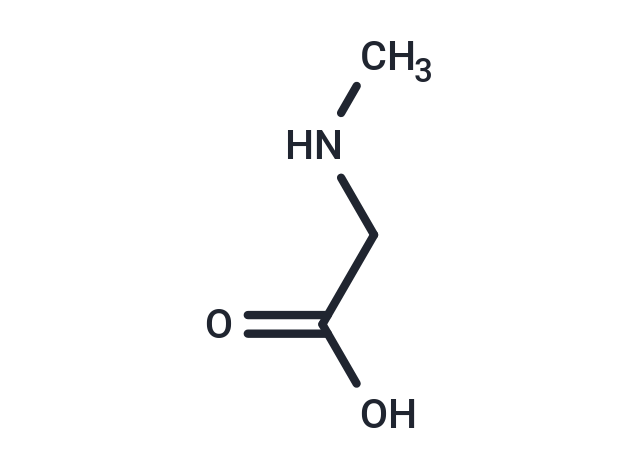
| Smiles | CNCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.093 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Insoluble H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.