Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

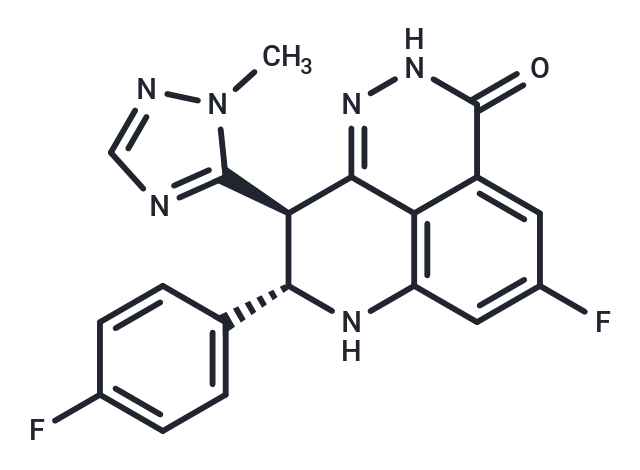
Talazoparib (LT-673) is a new-type PARP inhibitor (IC50: 0.58 nM), It similarly binds to PARP1/2 (Kis: 1.2/0.85 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $81 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $137 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $197 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $328 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $452 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $733 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $62 | In Stock |
| Description | Talazoparib (LT-673) is a new-type PARP inhibitor (IC50: 0.58 nM), It similarly binds to PARP1/2 (Kis: 1.2/0.85 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | PARP1:1.2 nM (Ki, cell free), PARP2:0.87 nM (Ki, cell free) |
| In vitro | Talazoparib (BMN 673) demonstrates excellent potency, inhibiting PARP1 and PARP2 enzyme activity with Ki = 1.2 and 0.87 nM, respectively. It inhibits PARP-mediated PARylation in a whole-cell assay with an EC50 of 2.51 nM and prevents the proliferation of cancer cells carrying mutant BRCA1/2, with EC50 = 0.3 nM (MX-1) and 5 nM (Capan-1), respectively [1]. BMN 673 is a potent PARP1/2 inhibitor (PARP1 IC50 = 0.57 nmol/L), but it does not inhibit other enzymes that we have tested. BMN 673 selectively targeted tumor cells with BRCA1, BRCA2, or PTEN gene defects with 20- to more than 200-fold greater potency than existing PARP1/2 inhibitors [2]. |
| In vivo | Talazoparib is orally available, displaying favorable pharmacokinetic (PK) properties and remarkable antitumor efficacy in the BRCA1 mutant MX-1 breast cancer xenograft model following oral administration as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy agents such as temozolomide and cisplatin [1]. Oral administration of BMN 673 elicited remarkable antitumor activity in vivo; xenografted tumors that carry defects in DNA repair due to BRCA mutations or PTEN deficiency were profoundly sensitive to oral BMN 673 treatment at well-tolerated doses in mice. Synergistic or additive antitumor effects were also found when BMN 673 was combined with temozolomide, SN38, or platinum drugs [2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The ability of a test compound to inhibit PARP1 enzyme activity was assessed using the PARP Assay Kit following the manufacturer's instruction. IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism5 software. For PARP inhibitor Ki determination, enzyme assays were conducted in 96-well FlashPlate with 0.5 U PARP1 enzyme, 0.25× activated DNA, 0.2 μCi [3H] NAD, and 5 μmol/L cold NAD in a final volume of 50 μL reaction buffer containing 10% glycerol (v/v), 25 mmol/L HEPES, 12.5 mmol/L MgCl2, 50 mmol/L KCl, 1 mmol/L dithiothreitol (DTT), and 0.01% NP-40 (v/v), pH 7.6. Reactions were initiated by adding NAD to the PARP reaction mixture with or without inhibitors and incubated for 1 minute at room temperature. Fifty microliter of ice-cold 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was then added to each well to stop the reaction. The plate was sealed and shaken for a further 120 minutes at room temperature, followed by centrifugation. Radioactive signal bound to the FlashPlate was determined using TopCount. PARP1 Km was determined using Michaelis–Menten equation from various substrate concentrations (1–100 μmol/L NAD). Compound Ki was calculated from enzyme inhibition curve according to the formula: Ki = IC50/[1+(substrate)/Km]. Km for PARP2 enzyme and compound Ki were determined with the same assay protocol except 30 ng PARP2, 0.25× activated DNA, 0.2 μCi [3H] NAD, and 20 μmol/L cold NAD were used in the reaction for 30 minutes at room temperature [2]. |
| Cell Research | Colony formation assays were conducted as described previously. In brief, cells were seeded into 6-well plates at a concentration of 500 to 2,000 cells per well. After 24 hours, media was replaced with fresh media containing PARP1/2 inhibitor. This procedure was repeated twice weekly for 14 days, at which point colonies were fixed with TCA and stained with sulforhodamine B. Colonies were counted and surviving fractions calculated by normalizing colony counts to colony numbers in vehicle-treated wells. Survival curves were plotted using a four-parameter logistic regression curve fit [2]. |
| Animal Research | Female athymic nu/nu mice (8–10-week old) were used for all in vivo xenograft studies. Mice were quarantined for at least 1 week before experimental manipulation. Exponentially growing cells (LNcap and MDA-MB-468) or in vivo passaged tumor fragments (MX-1) were implanted subcutaneously at the right flank of nude mice. When tumors reached an average volume of approximately 150 mm^3, mice were randomized into various treatment groups (6–8 mice/group) in each study. Mice were visually observed daily and tumors were measured twice weekly by calliper to determine tumor volume using the formula [length/2] × [width^2]. Group median tumor volume (mm^3) was graphed over time to monitor tumor growth. In single-agent studies, olaparib (100 mg/kg), BMN 673 (various doses as indicated), or vehicle (10% DMAc, 6% Solutol, and 84% PBS) was administered by oral gavage (per os), once daily or BMN 673 (0.165 mg/kg) twice daily for 28 consecutive days. Mice were continuously monitored for 10 more days after last day of dosing. In cisplatin combination study, BMN 673, olaparib, or vehicle was administered per os once daily for 8 days starting on day 1. Cisplatin at a dosage of 6 mg/kg or its vehicle (saline) was administered intraperitoneally as a single injection on day 3, 30 minutes after PARP inhibitor was administered. Combination with carboplatin was conducted in a similar way in MX-1 model in which BMN 673 was administered per os once daily for either 8 days or 5 days and carboplatin was injected intraperitoneally at single dose of 35 mg/kg, 30 minutes after BMN 673 on day 3 [2]. |
| Alias | LT-673, BMN-673 |
| Molecular Weight | 380.35 |
| Formula | C19H14F2N6O |
| Cas No. | 1207456-01-6 |
| Smiles | Cn1ncnc1[C@@H]1[C@H](Nc2cc(F)cc3c2c1n[nH]c3=O)c1ccc(F)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.63 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 36 mg/mL (94.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 0.1 mg/mL (0.26 mM), In vivo: Please add co-solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.