- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Tetracycline hydrochloride
Catalog No. T0912Cas No. 64-75-5
Alias Tetracycline HCl, NCI-c55561
Tetracycline hydrochloride (NCI-c55561) is the hydrochloride salt of the tetracycline, a broad-spectrum naphthacene antibiotic produced semisynthetically from chlortetracycline, an antibiotic isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces aureofaciens. In bacteria, tetracycline blocks binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis and bacterial cell growth. Because naturally, fluorescing tetracycline binds to a newly formed bone at the bone/osteoid interface, tetracycline-labeling of bone and fluorescence microscopy may be used to perform bone histomorphometry.
Tetracycline hydrochloride
Catalog No. T0912Alias Tetracycline HCl, NCI-c55561Cas No. 64-75-5
Tetracycline hydrochloride (NCI-c55561) is the hydrochloride salt of the tetracycline, a broad-spectrum naphthacene antibiotic produced semisynthetically from chlortetracycline, an antibiotic isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces aureofaciens. In bacteria, tetracycline blocks binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis and bacterial cell growth. Because naturally, fluorescing tetracycline binds to a newly formed bone at the bone/osteoid interface, tetracycline-labeling of bone and fluorescence microscopy may be used to perform bone histomorphometry.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $59 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Purity:99.43%
Contact us for more batch information
All TargetMol products are for research purposes only and cannot be used for human consumption. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use TargetMol products for any other purpose.Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | Tetracycline hydrochloride (NCI-c55561) is the hydrochloride salt of the tetracycline, a broad-spectrum naphthacene antibiotic produced semisynthetically from chlortetracycline, an antibiotic isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces aureofaciens. In bacteria, tetracycline blocks binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the mRNA-ribosome complex, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis and bacterial cell growth. Because naturally, fluorescing tetracycline binds to a newly formed bone at the bone/osteoid interface, tetracycline-labeling of bone and fluorescence microscopy may be used to perform bone histomorphometry. |
| In vitro | Tetracyclines are versatile broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against a vast array of organisms, including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as atypical pathogens like chlamydiae, mycoplasmas, rickettsiae, and protozoan parasites. Their mechanism of action involves blocking bacterial protein synthesis by hindering the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the bacterial ribosome. Specifically, in gram-negative enteric bacteria, tetracyclines enter through OmpF and OmpC porin channels as positively charged coordination complexes, likely involving magnesium ([1]). |
| In vivo | Tetracyclines are utilized for managing infections in various livestock, including poultry, cattle, sheep, and swine, and in aquaculture species such as salmon, catfish, and lobsters[2]. In specific scenarios, such as treating large populations of commercially farmed poultry, these antibiotics may be administered directly through feed, water, or aerosols. Additionally, tetracyclines may serve to promote or enhance growth. |
| Alias | Tetracycline HCl, NCI-c55561 |
| Molecular Weight | 480.9 |
| Formula | C22H24N2O8·HCl |
| Cas No. | 64-75-5 |
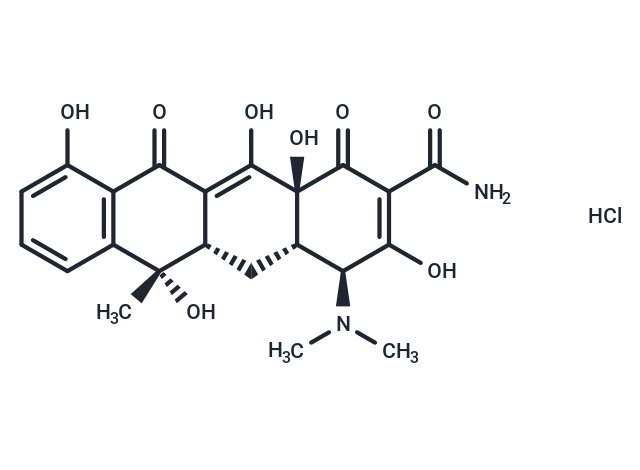
| Smiles | C[C@@]1([C@H]2C[C@H]3[C@@H](C(=C(C(=O)[C@]3(C(=C2C(=O)c2c1cccc2O)O)O)C(=O)N)O)N(C)C)O.Cl |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (93.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: 88 mg/mL (182.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sci Citations
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Keywords
Related Tags: buy Tetracycline hydrochloride | purchase Tetracycline hydrochloride | Tetracycline hydrochloride cost | order Tetracycline hydrochloride | Tetracycline hydrochloride chemical structure | Tetracycline hydrochloride in vivo | Tetracycline hydrochloride in vitro | Tetracycline hydrochloride formula | Tetracycline hydrochloride molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



