Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) is an essential fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body and is obtained by isolating it from seed oils. α-Linolenic acid has been shown to improve memory, inhibit thrombosis, and lower blood lipids.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | Inquiry | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $40 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $70 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | α-Linolenic Acid (ALA) is an essential fatty acid that cannot be synthesized by the human body and is obtained by isolating it from seed oils. α-Linolenic acid has been shown to improve memory, inhibit thrombosis, and lower blood lipids. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Osteosarcoma cells MG63, 143B and U2OS were treated with α-Linolenic Acid (10-200 µM) for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. RESULTS: α-Linolenic Acid showed a highly inhibitory effect on cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 51.69±0.14 µM in MG63 cells, 56.93±0.23 µM in 143B cells and 49.8±0.50 µM in U2OS cells.[1] METHODS: Breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 were treated with α-Linolenic Acid (25-100 µM) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometer. RESULTS: The percentage of apoptotic cells in the early (from 2.9% to 23.5% and from 5.5% to 16.7%, respectively) and late (from 0.6% to 3.4% and from 2.0% to 13.8%, respectively) apoptotic stages was significantly increased in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells treated with 100 µM α-Linolenic Acid. percentage significantly increased, which was significantly higher compared to untreated control cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the therapeutic effect on colitis in mice, α-Linolenic Acid (150-300 mg/kg, dispersed in 0.25% Tween-20) was administered by gavage to HFHSD-fed BABL/c mice once daily for nine weeks. At the end of nine weeks, experimental colitis was induced by intracolonic injection of TNBS. RESULTS: Low α-Linolenic Acid administration significantly ameliorated TNBS-induced clinical manifestations, body weight loss, spleen weight loss, and histologic damage. In contrast, high α-Linolenic Acid administration did not improve colitis and even exacerbated symptoms.HFHSD exacerbated TNBS-induced colitis via the Th1/Th17 pathway. Low α-Linolenic Acid showed a protective effect against TNBS-induced colitis via the Th1/Th2/Th17 pathway. [3] |
| Alias | Linolenic acid, Alpha-Linolenic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 278.43 |
| Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Cas No. | 463-40-1 |
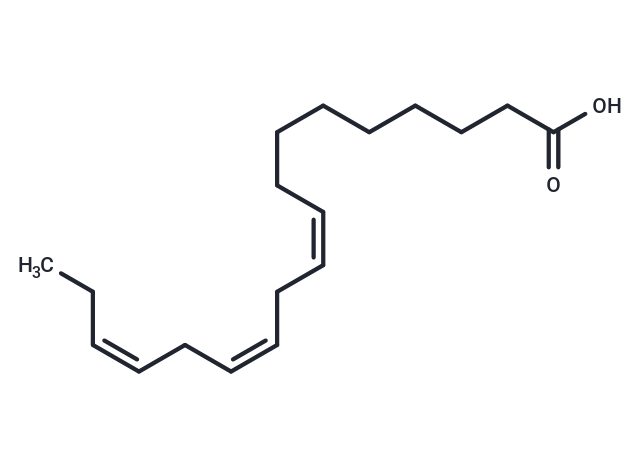
| Smiles | CC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.914 g/cm3 at 25℃ (lit.) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 100 mg/mL (359.16 mM), Sonication is recommended. 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 10 mg/mL (35.92 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 100 mg/mL (359.16 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.