Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BAY-876 is an orally active, selective inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1, IC50= 2 nM), exhibiting over 130-fold greater selectivity for GLUT1 than GLUT2, GLUT3, and GLUT4. It also inhibits glycolytic metabolism and ovarian cancer growth.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $79 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $148 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $273 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $449 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $659 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $108 | In Stock |
| Description | BAY-876 is an orally active, selective inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1, IC50= 2 nM), exhibiting over 130-fold greater selectivity for GLUT1 than GLUT2, GLUT3, and GLUT4. It also inhibits glycolytic metabolism and ovarian cancer growth. |
| Targets&IC50 | GLUT1:0.002 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: HNSCC cell lines SCC47 and RPMI2650 were treated with BAY-876 (0.01-100 µM) for 24 h. Cell viability was detected by crystal violet staining. RESULTS: After 24 h, BAY-876 reduced the viable SCC47 and RPMI2650 cells. [1] METHODS: Ovarian cancer cells SKOV-3, OVCAR-3 and HEY were treated with BAY-876 (25-75 nM) for 24 h. The rate of glycolysis was detected by Glycolysis Assay. RESULTS: Incubation with BAY-876 dose-dependently decreased the rate of glycolysis in SKOV-3, OVCAR-3 and HEY cells. Although this anti-glycolytic effect of BAY-876 was detectable at single-digit nanomolar concentrations, half-maximal inhibition was achieved at 25-50 nM of the compound. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect the antitumor activity in vivo, BAY-876 (1.5-4.5 mg/kg, 0.5% hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and 0.1% Tween 80) was administered by gavage to NSG mice bearing SKOV-3 xenografts once a day for four weeks. RESULTS: BAY-876 showed a significant dose-dependent inhibitory effect on tumorigenicity. The maximum effect was observed in the 4.5 mg/kg/day treatment group. After 2 weeks of treatment, tumors were significantly reduced. At the endpoint, final mean tumor volume and tumor weight decreased by 68% and 66%, respectively, compared to the excipient control group. However, the dose of 4.5 mg/kg/day was toxic to NSG mice. [2] |
| Molecular Weight | 496.42 |
| Formula | C24H16F4N6O2 |
| Cas No. | 1799753-84-6 |
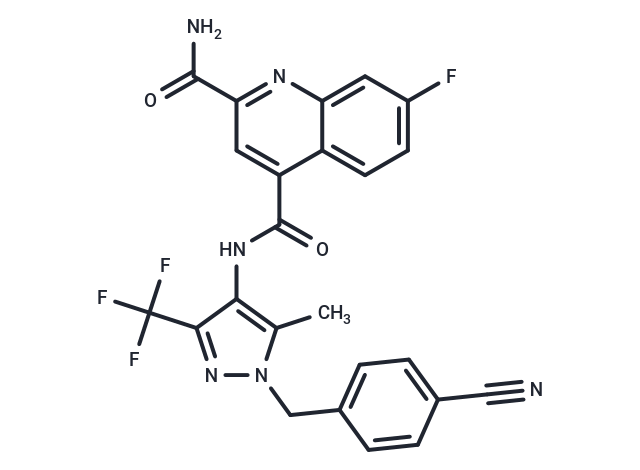
| Smiles | Cc1c(NC(=O)c2cc(nc3cc(F)ccc23)C(N)=O)c(nn1Cc1ccc(cc1)C#N)C(F)(F)F |
| Relative Density. | 1.48 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 3 mg/mL (6.04 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 15 mg/mL (30.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.