Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BX471 (BX 471) is a potent, selective non-peptide CCR1 antagonist.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $32 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $83 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $126 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $223 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $347 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $543 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $823 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $92 | In Stock |
| Description | BX471 (BX 471) is a potent, selective non-peptide CCR1 antagonist. |
| Targets&IC50 | CCR1:1 nM (Ki) |
| In vitro | BX 471 is a potent functional antagonist based on its ability to inhibit a number of CCR1-mediated effects including Ca2+ mobilization, increase in extracellular acidification rate, CD11b expression, and leukocyte migration. BX 471 demonstrats a greater than 10,000-fold selectivity for CCR1 compared with 28 G-protein-coupled receptors[1]. BX471 is also able to displace 125I-MIP-1α/CCL3 binding to mouse CCR1 in a concentration-dependent manner with a Ki of 215±46 nM. Increasing concentrations of BX471 inhibits the Ca2+ transients induced by MIP-1α/CCL3 in both human and mouse CCR1 with IC50 of 5.8±1 nM and 198±7 nM, respectively[2]. BX471 (0.1-10 μM) shows a dose-dependent inhibition of RANTES-mediated and shear-resistant adhesion on IL-1β-activated microvascular endothelium in shear flow in isolated blood monocytes. BX471 also inhibits the RANTES-mediated adhesion of T lymphocytes to activated endothelium[4]. |
| In vivo | BX 471, administered orally (p.o.) or intravenously (i.v.) at a dosage of 4 mg/kg, demonstrates an oral bioavailability of 60% in dogs and effectively mitigates symptoms in a rat model of multiple sclerosis, specifically the experimental allergic encephalomyelitis model[1]. When given subcutaneously (s.c.) at 20 mg/kg, BX 471 achieves peak plasma concentrations of 9 μM within approximately 30 minutes, subsequently decreasing to about 0.4 μM after 2 hours and further dropping to 0.1 μM or below from 4 to 8 hours. Treatment with 20 mg/kg BX 471 for 10 days in mice results in a 55% reduction in interstitial CD45 positive leukocytes. Although the effect on CCR5-positive CD8 cells in peripheral blood is marginally significant, BX 471 notably reduces FSP1-positive cells in UUO (unilateral ureteral obstruction) kidney conditions by 65% compared to controls[2], and pre-treatment with BX 471 significantly diminishes macrophage and neutrophil accumulation in the kidney following ischemia-reperfusion injury[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Kinase activity assays: In vitro activities of purified GST–NUAK1 and GST–NUAK1[A195T] are measured using Cerenkov counting of incorporation of radioactive 32P from [γ-32P]ATP into Sakamototide substrate peptide. Reactions are carried out in a 50 μL reaction volume for 30 min at 30°C and reactions are terminated by spotting 40 μL of the reaction mix on to P81 paper and immediately immersing in 50 mM orthophosphoric acid. Samples are washed three times in 50 mM orthophosphoric acid followed by a single acetone rinse and air drying. The kinase-mediated incorporation of [γ-32P]ATP into Sakamototide is quantified by Cerenkov counting. One unit of activity is defined as that which catalyses the incorporation of 1 nmol of [32P]phosphate into the substrate over 1 h. |
| Cell Research | Briefly, dermal microvascular endothelial cells grown to confluence in Petri dishes are stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL) for 12 h followed by pre-incubation with RANTES (10 nM) for 30 min at 37°C just prior to assay. The plates are assembled as the lower wall in a parallel wall flow chamber and mounted on the stage of an Olympus IMT-2 inverted microscope with ×20 and ×40 phase-contrast objectives. Isolated human blood monocytes are isolated and resuspended at 5×105?cells/mL in assay buffer (HBSS) containing 10 mM?HEPES, pH 7.4 and 0.5% human serum albumin. Shortly before the assay, 1 mM Mg2+?and 1 mM?Ca2+?are added. The cell suspensions are kept in a heating block at 37°C during the assay and perfused into the flow chamber at a rate of 1.5 dyn/cm2?for 5 min. For inhibition experiments, monocytes are preincubated with BX471 at different concentrations (0.1-10 μM) or a Me2SO control for 10 min at 37°C. The number of firmLy adherent cells after 5 min is quantitated in multiple fields (at least five per experiment) by analysis of images recorded with a long integration JVC 3CCD video camera and a JVC SR L 900 E video recorder and are expressed as cells/mm2. The type of adhesion analyzed is restricted to primary,?i.e.?direct interactions of monocytes with endothelium. |
| Alias | ZK-811752, BX-471, BX 471 |
| Molecular Weight | 434.89 |
| Formula | C21H24ClFN4O3 |
| Cas No. | 217645-70-0 |
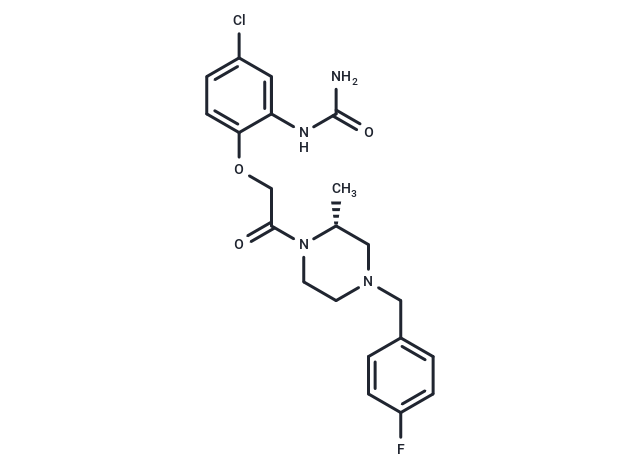
| Smiles | C[C@@H]1CN(Cc2ccc(F)cc2)CCN1C(=O)COc1ccc(Cl)cc1NC(N)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.346 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (399.4 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.