Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Bosentan hydrate (Ro 47-0203) is a competitive and dual antagonist of endothelin-1 at the endothelin-A (ET-A) and endothelin-B (ET-B) receptors.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $55 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $58 | In Stock |
| Description | Bosentan hydrate (Ro 47-0203) is a competitive and dual antagonist of endothelin-1 at the endothelin-A (ET-A) and endothelin-B (ET-B) receptors. |
| Targets&IC50 | ETB:95 nM(Ki), ETA:4.7 nM(Ki) |
| In vitro | Bosentan competitively antagonizes the specific binding of [125 I]-labeled ET-1 on human smooth muscle cells (ET-A receptors)human placenta (ET-B receptors). Bosentan also inhibits the binding of selective ET-B ligands on porcine trachea. Contractions induced by ET-1 in isolated rat aorta (ET-A) and by the selective ET-B agonist sarafotoxin S6C in rat trachea are competitively inhibited by Bosentan (pA2= 7.2 and 6.0, respectively), as is the endothelium-dependent relaxation to sarafotoxin S6C in rabbit superior mesenteric artery (pA2= 6.7). The binding of 40 other peptides, prostaglandins, ions and neurotransmitters is not significantly affected by Bosentan, which shows its specificity for ET receptors. [1] |
| In vivo | Bosentan inhibits the presser response to big ET-1 both after i.v. and oral administration, with a long duration of action and no intrinsic agonist activity. Bosentan also inhibits the depressor and presser effect of ET-1 and sarafotoxin S6C. Its pharmacological profile makes Bosentan a potentially useful drug in the management of clinical disorders associated with vasoconstriction.[1] Bosentan is the first oral non-peptide mixed ETA/B-receptor antagonist. Long-term treatment with Bosentan has markedly increased the survival, hemodynamics, and cardiac remodeling in rats with CHF. Bosentan decreases arterial BP to a similar degree as an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Administration of Bosentan in rats with CHF after acute MI significantly decreases arterial BP and has additive effect to that of an ACE inhibitor. Acute and chronical treatment with Bosentan also improves the systemic and pulmonary hemodynamics by a decrease in peripheral and pulmonary vascular resistance, and increase of cardiac output in patients with CHF. [2] |
| Cell Research | Bosentan is prepared in DMSO and diluted with appropriate medium before use[2]. Cell viability is evaluated by the trypan blue exclusion test. Human dermal fibroblasts are treated with the indicated concentration of Bosentan (10, 20 and 40 μM). Cell viability is examined at 24 and 48 hours. Stained (dead) and unstained (viable) cells are counted with a hematocytometer[2]. |
| Alias | Ro 47-0203, Bosentan Hydrate, Benzenesulfonamide, Actelion |
| Molecular Weight | 569.63 |
| Formula | C27H29N5O6S·H2O |
| Cas No. | 157212-55-0 |
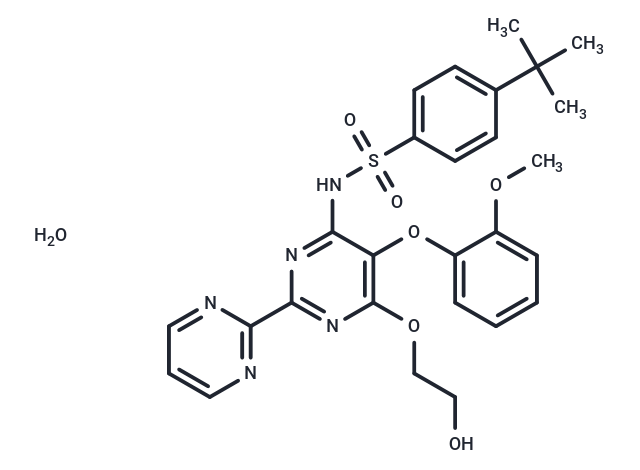
| Smiles | O.COC1=CC=CC=C1OC1=C(OCCO)N=C(N=C1NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C)(C)C)C1=NC=CC=N1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 93 mg/mL (163.26 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (3.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.