- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Ethionamide
Catalog No. T1165Cas No. 536-33-4
Alias Ethinamide, Bayer 5312, 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide
Ethionamide (2-ethylthioisonicotinamide) is a nicotinamide derivative, with antibacterial activity, used to treat tuberculosis. Although the exact mechanism of action of ethionamide is unknown, it may inhibit the synthesis of mycolic acid, a saturated fatty acid found in the bacterial cell wall, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. This eventually leads to bacterial cell wall disruption and cell lysis. Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the organism involved.
Ethionamide
Catalog No. T1165Alias Ethinamide, Bayer 5312, 2-ethylthioisonicotinamideCas No. 536-33-4
Ethionamide (2-ethylthioisonicotinamide) is a nicotinamide derivative, with antibacterial activity, used to treat tuberculosis. Although the exact mechanism of action of ethionamide is unknown, it may inhibit the synthesis of mycolic acid, a saturated fatty acid found in the bacterial cell wall, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. This eventually leads to bacterial cell wall disruption and cell lysis. Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the organism involved.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $51 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $81 | Backorder | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $53 | In Stock |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Purity:99.92%
Contact us for more batch information
All TargetMol products are for research purposes only and cannot be used for human consumption. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use TargetMol products for any other purpose.Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | Ethionamide (2-ethylthioisonicotinamide) is a nicotinamide derivative, with antibacterial activity, used to treat tuberculosis. Although the exact mechanism of action of ethionamide is unknown, it may inhibit the synthesis of mycolic acid, a saturated fatty acid found in the bacterial cell wall, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. This eventually leads to bacterial cell wall disruption and cell lysis. Ethionamide may be bacteriostatic or bactericidal in action, depending on the concentration of the drug at the site of infection and the susceptibility of the organism involved. |
| In vitro | Ethionamide is a structural analogue of isoniazid (INH), both are pro-drugs that need to be activated by mycobacterial enzymes to exert their antimicrobial activity. Ethionamide mechanism of action is thought to be identical to INH although the pathway of activation is distinct from that of INH. Ethionamide is activated by an EthA enzyme, leading to the formation of a Soxide metabolite that has considerably better activity than the parent drug. [1] Ethionamide inhibits both biofilm formation and viability of mature biofilms. Ethionamide reduces the content of ergosterol in Cryptococcus spp. planktonic cells and destabilized or permeabilized the fungal cell membrane, leading to leakage of macromolecules. [2] Ethionamide is in general toxic at concentrations above 0.50 mM to HepG2, Caco-2, and RAW macrophage cells, but the toxicity is drastically reduced when Ethionamide is loaded into the microparticles. Ethionamide shows a fast metabolization process in the presence of the thermally carbonized- Porous silicon (TCPSi) particles. [3] Ethionamide is activated in Mycobacterium tuberculosis by the protein encoded by the gene Rv3854c. Ethionamide appear to disrupt cell wall biosynthesis and have at least one common cellular target, the enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase InhA. [4] |
| Alias | Ethinamide, Bayer 5312, 2-ethylthioisonicotinamide |
| Molecular Weight | 166.24 |
| Formula | C8H10N2S |
| Cas No. | 536-33-4 |
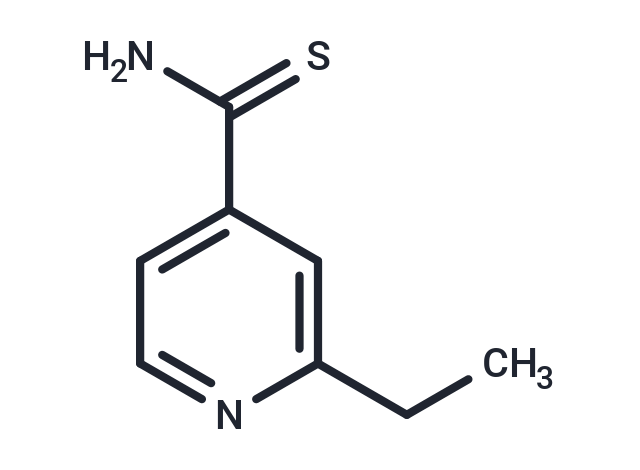
| Smiles | C(N)(=S)C=1C=C(CC)N=CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.17 g/cm3 |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 14 mg/mL (84.2 mM) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 75 mg/mL (451.15 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Related Tags: buy Ethionamide | purchase Ethionamide | Ethionamide cost | order Ethionamide | Ethionamide chemical structure | Ethionamide in vitro | Ethionamide formula | Ethionamide molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.




