Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

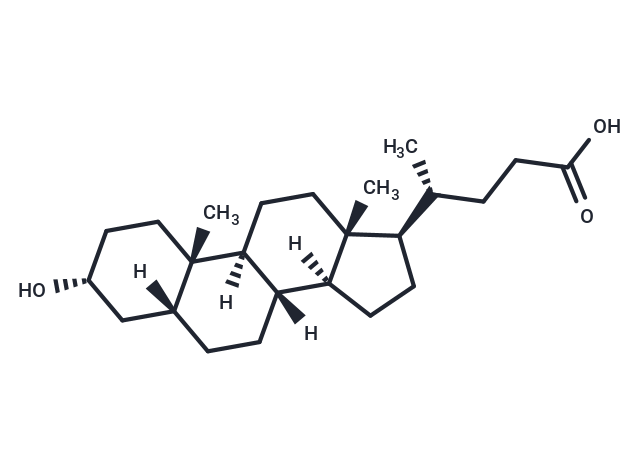
Lithocholic acid (3α-Hydroxy-5β-cholanic acid) is a bile acid formed from chenodeoxycholate by bacterial action, usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for absorption and is itself absorbed. It is used as cholagogue and choleretic.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $55 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $87 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Lithocholic acid (3α-Hydroxy-5β-cholanic acid) is a bile acid formed from chenodeoxycholate by bacterial action, usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It acts as a detergent to solubilize fats for absorption and is itself absorbed. It is used as cholagogue and choleretic. |
| In vitro | In a mouse cancer model induced by DMH (dimethylhydrazine), LCA effectively inhibits apoptosis almost completely in the precancerous colon. When administered to rodents, LCA and its conjugates cause intrahepatic cholestasis, a pathological state characterized by reduced bile flow and the accumulation of bile components in the liver and blood. Lithocholic acid activates the vitamin D receptor, inducing the expression of CYP3A, a cytochrome P450 enzyme that detoxifies LCA in the liver and intestines. |
| In vivo | Lithocholic acid exhibits tumor-promoting activity and inhibits mammalian DNA polymerase β with an IC50 of 15 μM. It causes cholestasis (cessation or obstruction of bile flow) within the liver. Furthermore, lithocholic acid activates the Pregnane X Receptor (PXR), and the severe liver damage induced by LCA can be mitigated by the activation of PXR. Additionally, lithocholic acid directly binds to the vitamin D receptor with a Ki of 29 μM, activating it with a sensitivity higher than that for other nuclear receptors (e.g., PXR, FXR), with a Ki of 30 μM. This activation offers protection from its toxic effects. |
| Kinase Assay | Competitive ligand binding assay.: Ligand binding is performed using lysates from COS-7 cells transfected with expression plasmids for VDR or RXRα. Binding is performed overnight at 4°C in lysate buffer with 0.71 nM (18 Ci/mmol) [3H]1,25(OH)2D3 and bile acid competitor. Unbound [3H]1,25(OH)2D3 is removed by adsorption to dextran-coated charcoal and the supernatant removed for scintillation counting. Ki values are calculated from a computer fit of competition curves from triplicate assays. |
| Alias | 3α-Hydroxy-5β-cholanic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 376.57 |
| Formula | C24H40O3 |
| Cas No. | 434-13-9 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCC(O)=O)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@]1([H])[C@@]2([H])CC[C@]2([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]12C |
| Relative Density. | 1.0454 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 44 mg/mL (116.84 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (146.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.