Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Avasimibe (PD-148515) is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of acyl-Coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT, IC50: 3.3 μM) that prevents cholesterol deposition in the arterial wall. It also inhibits human P450 isoenzymes CYP2C9/1A2/2C19 (IC50: 2.9/13.9/26.5 μM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $43 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $82 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $148 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $263 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $425 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock |
| Description | Avasimibe (PD-148515) is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of acyl-Coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT, IC50: 3.3 μM) that prevents cholesterol deposition in the arterial wall. It also inhibits human P450 isoenzymes CYP2C9/1A2/2C19 (IC50: 2.9/13.9/26.5 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | ACAT:3.3 μM, CYP2C19:26.5 μM, CYP1A2:13.9 μM, CYP2C9:2.9 μM |
| In vitro | In HepG2 cells incubated for 24 h, Avasimibe (0.01/1/10 μM) reduced ApoB secreted into the culture medium by 25%, 27% and 43%, respectively. In human monocyte-derived macrophages, Avasimibe (1 μg/ml) lowered esterified and total cholesterol by inhibiting LDL binding and reducing scavenger receptor counts during the foam cell formation phase.Pre-warming of Avasimibe (2 μg/ml) with LDL (10 μg/ml) resulted in enhanced cholesterol efflux from HMM foam cells. Avasimibe decreases ApoB secretion by enhancing intracellular ApoB degradation, but does not affect its ApoB synthesis. In IC-21 macrophages, Avasimibe inhibited ACTC (IC50: 3.3 μM). In glioma cells, Avasimibe inhibited cholesteryl ester synthesis and ACAT-1 expression. Avasimibe inhibited glioma cell growth by inducing apoptosis caused by cell cycle arrest and caspase-8/3 activation.Avasimibe dose-dependently inhibited lipoprotein(a) accumulation in primary monkey liver cell cultures (11.9% -31.3%), which was associated with a decrease in ApoA. |
| In vivo | In HepG2 cells incubated for 24 h, Avasimibe (0.01/1/10 μM) reduced ApoB secreted into the culture medium by 25%, 27% and 43%, respectively. In human monocyte-derived macrophages, Avasimibe (1 μg/ml) lowered esterified and total cholesterol by inhibiting LDL binding and reducing scavenger receptor counts during the foam cell formation phase.Pre-warming of Avasimibe (2 μg/ml) with LDL (10 μg/ml) resulted in enhanced cholesterol efflux from HMM foam cells. Avasimibe decreases ApoB secretion by enhancing intracellular ApoB degradation, but does not affect its ApoB synthesis. In IC-21 macrophages, Avasimibe inhibited ACTC (IC50: 3.3 μM). In glioma cells, Avasimibe inhibited cholesteryl ester synthesis and ACAT-1 expression. Avasimibe inhibited glioma cell growth by inducing apoptosis caused by cell cycle arrest and caspase-8/3 activation.Avasimibe dose-dependently inhibited lipoprotein(a) accumulation in primary monkey liver cell cultures (11.9% -31.3%), which was associated with a decrease in ApoA. |
| Kinase Assay | P450 Inhibition Studies: Pooled human liver microsomes (HLM) from at least 15 donors are used for all inhibition assays. For IC50 determinations, the substrate probes are used at their approximate in vitro Km values. All incubations are performed with 100 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) and 1 mM NADPH. For CYP1A2 inhibition study, incubations are performed in a total volume of 0.5 ml, in duplicates with 0.1 mg/ml HLM, 30 μM phenacetin, 1 mM NADPH, and in the presence of avasimibe (0, 0.3, 0.75, 1.5, 3, 7.5, 15, 30, and 40 μM in 50 mM) in a potassium phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. After preincubation at 37 °C for 7 min, NADPH is added to initiate the enzyme reaction. The reaction mixture is quenched with 500 μl of ice-cold 100 ng/ml paracetamol-D4/CH3CN after 25 min. The standards (4-acetamidophenol, singlet) and quality controls (triplicates for low, medium, and high) are prepared at room temperature. After mixing, 0.2 ml of the samples is transferred to another plate and submitted for LC/MS/MS analysis after centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min. A Supelco Discovery Amide C16, 100 × 2.1 mm (5-μm particle size) column (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA) is used. The mobile phase is isocratic, 40:60 [acetonitrile/formic acid, 0.1% (v/v)] at 0.2 ml/min. |
| Cell Research | For foam cell formation, the growth medium (RPMI medium containing 10% human serum) is aspirated and the BMMs are rinsed four times with RPMI medium, and then HMMs are exposed to RPMI medium containing bovine serum albumin (BSA, 0.2%) and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO, 0.2%, vehicle for CI-1011) (control medium) with and without agacLDL (100 μg protein/ml) and CI-1011 (1 μg/ml) for 48 hours. For cholesterol efflux experiments, HMMs are preincubated with ag-acLDL (100 μg protein/ml) for 24h, and then exposed to control RPMI medium with and without HDL (100 μg protein/ml), CI-1011 (2 μg/ml) or HDL plus CI-1011 (2 μg/ml) for 24–48 hours. Additionally, the appearance of [14C]FC in the medium is monitored by first preincubating HMMs with RPMI medium containing ag-acLDL (100 μg protein/ml) radiolabeled with [4-14C]FC (0.5 μCi/ml) in an ethanolic spritz (final concentration, 0.1%) for 24 h. The medium is removed, cells rinsed three times with RPMI medium, and then cells are exposed to control RPMI medium with and without CI-1011 (1–10 μg/ml) for 4–48 h. At each time point, the medium is aspirated and centrifuged to pellet nonadherent cells. The appearance of [14C]FC in the medium is measured by liquid scintillation spectroscopy. Cellular lipids are extracted using hexane:isopropanol (3:2, v/v) for 1 h. The distribution of cellular radiolabeled cholesterol is measured by subjecting an aliquot of the cell extract and FC and EC standards to thin layer chromatography using petroleum ether:hexane:glacial acetic acid solvent system (85:15:2, v/v). The percent FC efflux is calculated as: medium [14C]FC dpm/ cell [14C] dpm×100. FC and TC mass are quantified by gas liquid chromatography using stigmasterol (1 mg/ml) as an internal standard. EC mass is calculated as the difference between TC and FC, and all values are normalized to cell protein. The MBC is de?ned as the lowest concentration that exhibited 99.9% or more reduction of the numbers of colonies compared with the cfu in the initial inoculum. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | PD-148515, CI-1011 |
| Molecular Weight | 501.72 |
| Formula | C29H43NO4S |
| Cas No. | 166518-60-1 |
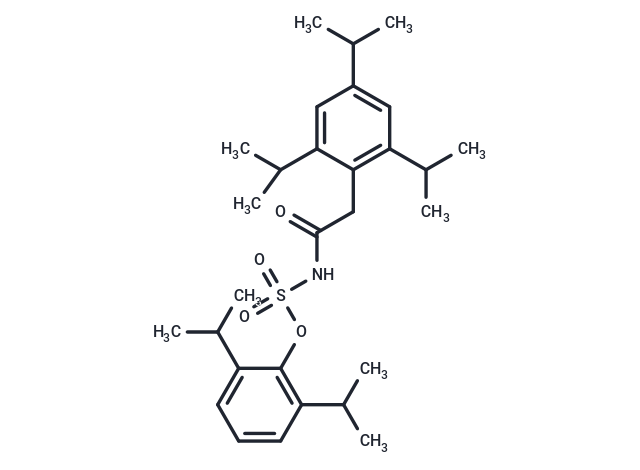
| Smiles | CC(C)c1cc(C(C)C)c(CC(=O)NS(=O)(=O)Oc2c(cccc2C(C)C)C(C)C)c(c1)C(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.072 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (199.31 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (3.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.